World AMR Week: The Fight Against Resistance
Introduction
World Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) Awareness Week is observed annually from November 18th to 24th to raise awareness, spread awareness, and educate people about antimicrobial resistance.
In 2015, the World Health Organization (WHO) initiated and launched World Antibiotic Awareness Week, which mainly focused on antibiotic resistance and raised understanding of the responsible use of antibiotics.
In 2020 the campaign was rebranded as World Antimicrobial Awareness Week in response to increasing recognition of resistance. The change now had a broader scope and included antivirals, antiparasitic, and antifungal medications.
Every year World Antimicrobial Awareness Week features a particular theme that emphasizes distinct aspects of antimicrobial resistance. The theme for the 2024 World Antimicrobial Awareness Week is Educate. Advocate. Act Now. The theme highlights the crucial need to raise awareness and education for combating antimicrobial resistance. [1]
What is Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR)?
Antimicrobial resistance occurs when viruses, bacteria, parasites, and fungi become resistant to medicines, rendering them ineffective. This makes infections difficult to treat and significantly increases the risk of disease spread. Due to drug resistance, infections have become considerably more challenging to treat and manage. [2]
Antimicrobial resistance is a serious global health issue and a socio-economic crisis. It profoundly impacts human and animal health, food systems, and the environment. The World Health Organization (WHO) identifies antimicrobial resistance (AMR) as one of the top ten global public health challenges [3] as per the estimations, it can result in 10 million deaths every year and can cost around $100 trillion to the global economy by the year 2050. [4]
Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) and healthcare systems
Antimicrobial resistance exerts a significant strain on healthcare systems. As per the studies, antimicrobial resistances lead to extreme financial consequences, including increased healthcare costs because of high hospital admissions, longer stays, increased units for intensive care, expensive therapies, and isolation beds. [3]
Healthcare professionals are also compelled to resort to antibiotics that are unconventional or combinations of various antibiotics for managing infections. These treatments can be increasingly expensive and may lead to several side effects. [3]
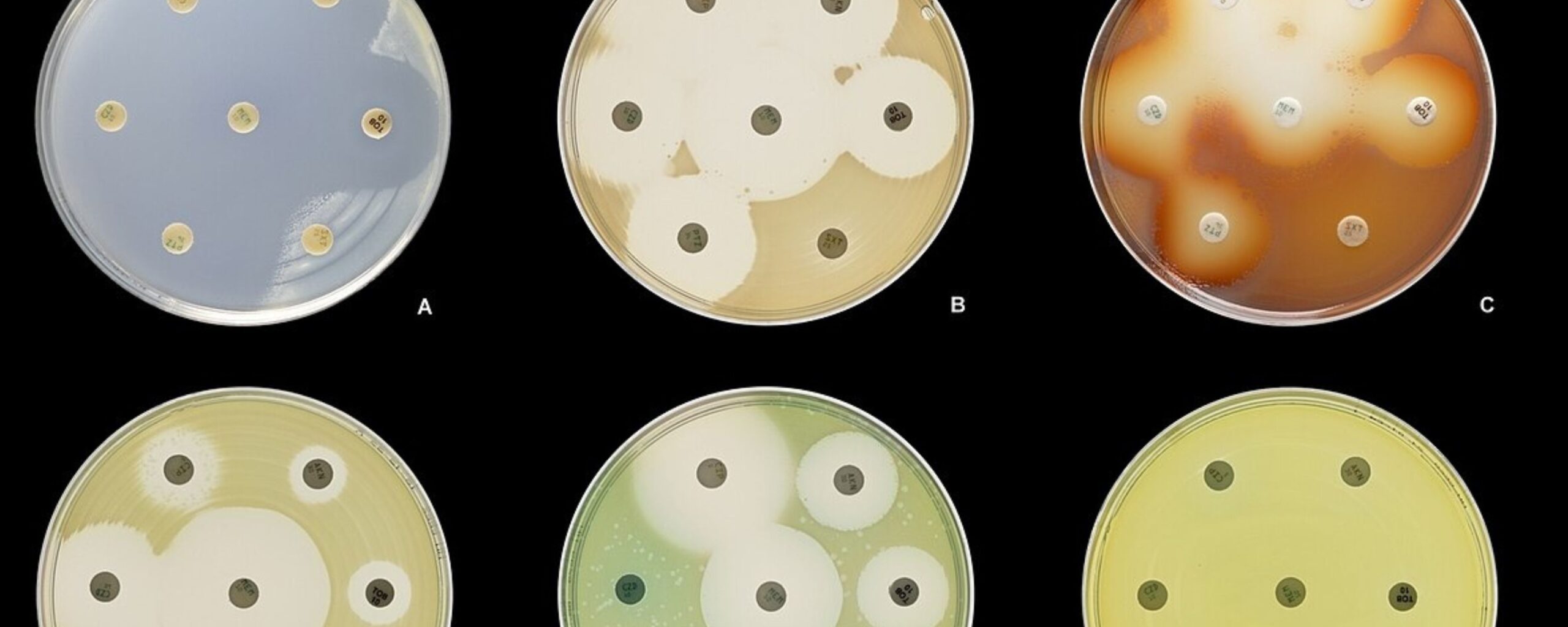
Why is it important to use Antimicrobials correctly?
Antimicrobials are lifesaving only when they work against the microbes that cause the disease or infection.
Like most medications, improper or excessive use of antimicrobials not only affects the patient undergoing treatment but also impacts the community in the future. Antimicrobial use eventually does lead to resistance, however, because of the overuse of antimicrobials there has been an acceleration in this process. Hence many antimicrobials have become ineffective and can no longer be used for treating infections. [5]
- It is crucial to take antimicrobials as prescribed by the doctor
- Patients must not pressure the doctors for antimicrobials if they feel they are not required
- Antimicrobial prescriptions must not be saved for later use nor someone should take another person’s antimicrobials without accurate information about the correct dosage [5]
Preventing Antimicrobial resistance (AMR)
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) can affect people at any stage of life as well as the agricultural and veterinary industries. AMR infections requiring second or third-line treatments may lead to serious side effects. Many medical procedures such as joint replacements, transplants cancer therapies, etc are highly dependent on the capability to fight infections with the help of antibiotics. In some instances, no effective treatments are available for infections caused by antimicrobial resistance. Hence it is crucial to make efforts towards preventing antimicrobial resistance. [6]
Some ways that can help prevent infections:
- Practice healthy Hygiene and Wash Hands
- Be informed about the symptoms and learn to recognize the early signs, approach a physician if you think you have the infection
- Use antimicrobials correctly
- Do not share or use leftover antimicrobials
- Get recommended vaccinations timely
- Prevent STIs [7]
- World AMR Awareness Week | WHO
- 18 to 24 November is World AMR Awareness Week | WHO
- Antimicrobial resistance and its impact on cancer care | Union for International Cancer Control (UICC)
- World AMR Awareness Week (WAAW) | UICC
- World AMR Awareness Week | Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Healthcare
- Controlling the Emergence and Spread of Antimicrobial Resistance | CDC.GOV
- Antibiotic Resistance | National Foundation for Infectious Diseases