Organic Farming: Eco-Friendly and Sustainable Agricultural Practices
Organic Farming: An Eco-Friendly Option
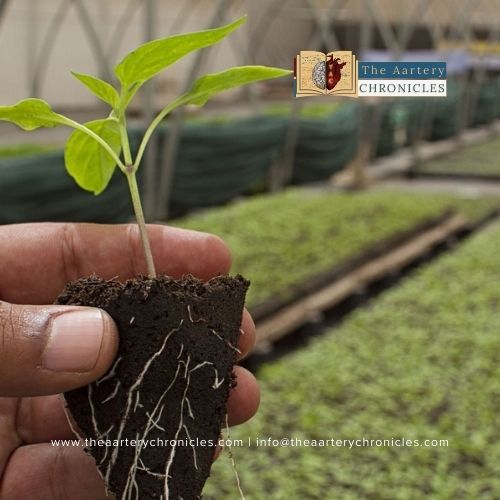
Organic farming involves cultivating crops and rearing animals using natural resources, eschewing synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, insecticides, and genetically modified organisms. The objective is to utilize energy and natural resources, maintain biodiversity, and promote animal welfare, fostering ecological balance.
Recognized as the Father of Modern Organic Agriculture, British Botanist Sir Albert Howard drew inspiration from traditional Indian farming practices. He has worked as an agriculturist in India and is well-versed in the traditional and sustainable farming practices learned here. Successfully adopting these practices, he has implemented them in the West. In our current scenario, rampant pollution and the presence of harmful chemicals in conventional agriculture make organic farming a healthier alternative. It minimizes harm to the soil and reduces farmers’ exposure to toxic chemicals in the air, water, and on the farms, making them less susceptible to diseases.
1o Key Advantages of Organic Farming
- Inexpensive: The avoidance of costly chemical fertilizers, pesticides, insecticides, and high-yielding variety (HYV) seeds for crop plantation makes organic farming an economical choice. No extra expense is required for planting the crops.
- Growing demand: With a growing health consciousness and a desire for healthy food, there is an increased demand for organic food in India and around the world. This surge in demand not only generates substantial income but also leads to an increase in exports.
- Nutritional: Organic food is more nutritious, palatable and healthy as compared to foods that use chemical compounds.
- Eco-friendly: Organic farming, being free of chemical compounds, emerges as an environmentally friendly practice that preserves both the ecosystem and the green layer. The reduced usage of chemicals not only improves and preserves soil quality but also contributes to carbon sequestration.
- Increased Employment: Organic farming demands extensive care, involving a vast and intricate process. Consequently, it requires a higher number of labourers. This surge in demand for labour is indicative of increased employment opportunities.
- Self-sufficiency: Farmers benefit economically, becoming self-sufficient and capable of providing better for their families.
- Minimal Pollution: Organic methods significantly lower pollution levels, resulting in cleaner, cooler atmospheres.
- Wildlife habitat: Increased green cover benefits wildlife, fostering a cleaner and more hospitable environment.
- Healthy food: Organic products stand out for their health benefits, being devoid of harmful chemicals, insecticides, pesticides, and genetically modified organisms.
- Energy conservation: Organic farms employ less energy-intensive methods, effectively reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
However, expanding the organic farming market demands attention to key aspects. This includes increasing output, ensuring affordability of final products, raising awareness about the benefits of organic crops, streamlining certification processes, and addressing concerns about the relatively shorter shelf life due to the absence of artificial preservatives
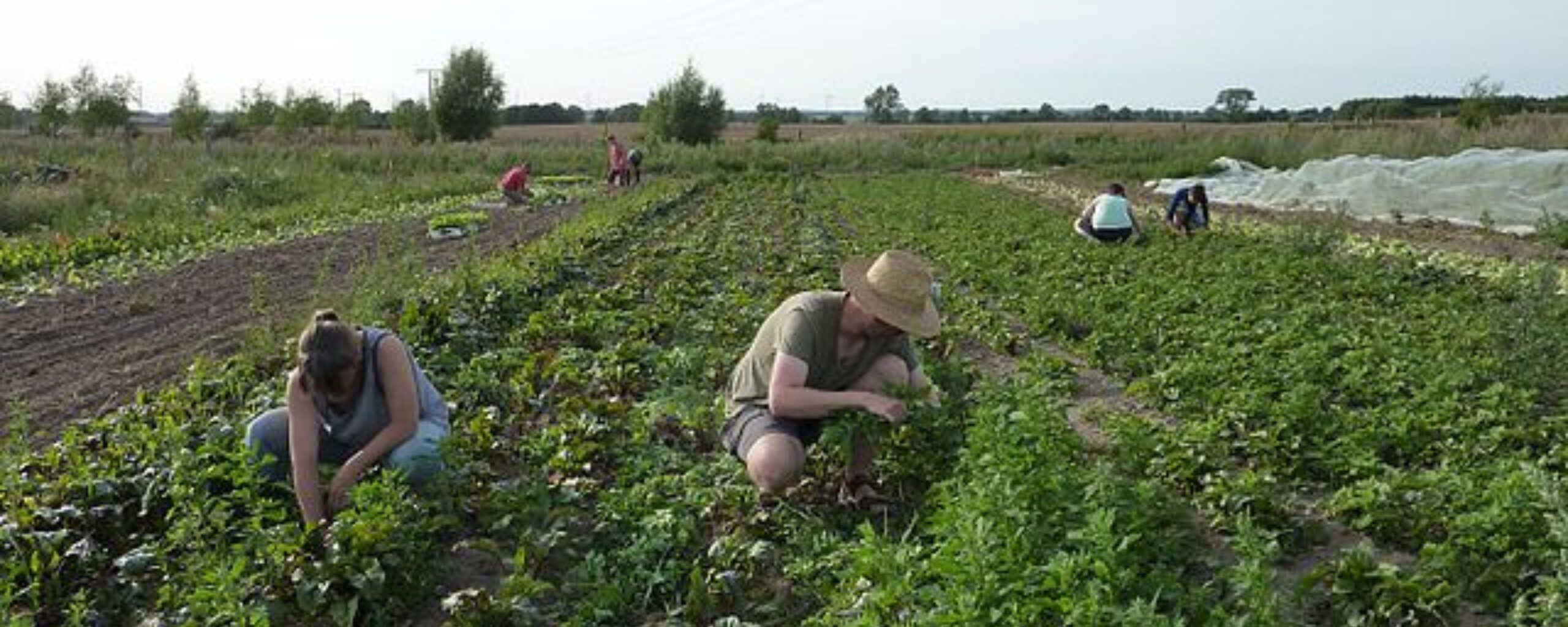

Methods of Organic Farming in India:
- Crop-based organic farming: In this method, the farmers use natural fertilizers like compost and manure, increase the soil fertility by crop rotation methods and use beneficial insects as sustainable pest control options.
- Livestock-based organic farming: In this method, animals are raised in eco-friendly and compassionate environments. They are given organic food, graze in open pastures and are not given antibiotics or growth hormones.
- Mixed organic farming: This method is an amalgamation of both crop-based and livestock-based organic farming. The collaboration of crop residues and livestock manure works synergistically to enrich the soil and reduce waste.
- Traditional farming: In this method, farmers adhere to time-tested practices that align with organic principles. These include the use of cow dung and manure, crop rotation, and natural pest control.
- Zero Budget Natural Farming (ZBNF): Developed over years of research and trial and error by Padmashri Shri Subhash Palekar, this method boasts a zero cost of growing and harvesting plants. Farmers eliminate the need for chemically potent fertilizers, pesticides, and insecticides by relying on cow dung and cow urine to enhance soil fertility and nutrient value.
- Organic Horticulture: Employed to cultivate organic orchards and gardens, this method focuses on producing chemical-free and healthier fruits and vegetables by utilizing only natural ingredients.

Sustainable Practices in Organic Farming:
In addition to these, some methods of Organic Farming are practised to sustain the soil health and natural processes.
- Jeevanmrutha: In this method, a fermented microbial culture made of cow dung, cow urine, jaggery and pulses is used as a fertilizer.
- Bijamrutha: In this method, a culture of seeds and cow dung is used as a natural fertilizer.
- Mulching: In this method, crop residue like mulch is used to conserve soil moisture, suppress weeds and improve soil quality.
- Crop Rotation: In this method, the crops are grown in rotation which eliminates pests and diseases contained in the soil. Mixed cropping, intercropping and agroforestry methods are also employed to increase land use and reduce environmental impact.
- Vermicomposting: In this method, the earthworms aid in breaking down the organic matter into rich and nutrient-laden compost.
- Biofertilizers like rhizobium for legumes and mycorrhizal fungi are used to increase the nutrient availability to the plants.
- Microbial inoculants like Trichoderma and Pseudomonas are used to protect the plants from disease and promote growth.
- Natural pest control: Utilizing neem-based pesticides, biopesticides, and biological agents such as ladybugs and spiders proves to be an effective method for protecting plants and crops from pests. Additionally, techniques like companion planting and trap cropping are employed to naturally eliminate pests.
- Seed saving: Traditional, heirloom seeds are preserved and are adapted locally to maintain genetic diversity. Initiatives like community seed banks foster the exchange and conservation of these traditional seeds.
- Organic livestock: In this method, cow dung and urine are used as natural manure and cow-based farming (Gauvansh) is also being practised. Moreover, the practice involves raising indigenous and non-exotic livestock for organic feed.
- Tillage: Conserving techniques like zero tillage and minimum tillage reduce soil erosion and enhance moisture retention in arid regions.

Organic farming, as we can see, has various benefits and this industry is growing by leaps and bounds. The forests thrive naturally, as we know, therefore we can definitely make a conscious effort to use our natural resources and protect our environment simultaneously. Why disturb the balance of Mother Nature, when we can preserve it?
Sikkim, a North East Indian state, achieved the remarkable feat of becoming India’s first fully organic state in 2016. This achievement is a testament to the foresight and long-term planning initiated in 2003. Sikkim’s commitment to sustainable agriculture has earned it the ‘Oscar for best policies’ from the Food and Agriculture Organization, highlighting its role as a global leader in promoting agro-ecological and sustainable food systems. Truly a ‘Make in India’ success story!”
As of 2021, India holds the 6th position globally in terms of organic agricultural land and proudly claims the 1st position in the total number of producers. This data, sourced from the FIBL & IFOAM Year Book 2023, underscores India’s significant contribution to the world of organic farming.
Mehrotra Consumer Products Pvt. Ltd. stands as a leading force in the organic food industry, renowned for producing and supplying a diverse range of organic food products under the esteemed brand name ‘Down to Earth’.
Compliance with essential legalities, including securing certification from APEDA (The Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority), is imperative for the export of organic products. In this burgeoning industry, rigorous inspection and certification by accrediting agencies ensure the fitness of products for international export
In the profound words of Sadhguru (Jaggi Vasudev), ‘With wrong farming methods, we turn fertile land into desert. Unless we go back to organic farming and save the soil, there is no future.’ This underscores the critical role of organic practices in safeguarding our agricultural landscapes.”

Author: Ms Rupal Sonpal
- Medicine and Diseases
- Nutrition and Diet