Nikshay Poshan Yojana: India’s Initiative to Combat Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) remains a major global health threat, leading to millions of deaths each year in India alone. The disease presents a significant public health concern in India, with millions of new cases reported annually. Recognizing the urgent need to address the nutritional needs of TB patients and improve treatment outcomes, the government of India launched the Nikshay Poshan Yojana in April 2018. This groundbreaking initiative, implemented under the National Tuberculosis Elimination Program (NTEP), aims to provide nutritional support to TB patients, thereby enhancing their health and well-being.
Current Status of Tuberculosis in India
The burden of tuberculosis (TB) in India remains substantial, with the country being one of the most heavily affected globally. Here’s an overview of the TB burden in India:
- Prevalence: The National Prevalence Survey of India conducted between 2019 and 2021 found that approximately 31% of individuals aged 15 and above carry the burden of tuberculosis infection (TBI). [1]
- Incidence rate: In 2021, India recorded a tuberculosis (TB) incidence rate of 210 per 100,000 population, positioning the country at the 36th spot globally in terms of TB incidence rates. India’s endeavours have led to a 16% decrease in TB incidence in 2022 compared to 2015, nearly twice the global rate of decline, which stands at 8.7%. [2]
- Mortality rate: TB mortality has decreased by 18% since 2015, both in India and globally. The World Health Organization revised the tuberculosis mortality rate, dropping from 494,000 in 2021 to 331,000 in 2022, marking a reduction of over 34%. [3]
Understanding the Nikshay Poshan Yojana (NYP)
The Nikshay Poshan Yojana, also known as National Support to TB patients, is an incentive scheme launched by the Central TB Division of the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MoHFW) under the National Tuberculosis Elimination Program (NTEP). In April 2018, the Government of India launched the Nikshay Poshan Yojana (NPY) as a scheme under Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT), providing monthly financial aid for nutrition to TB patients.
The scheme aims to provide financial assistance and support to tuberculosis (TB) patients undergoing treatment, with the overarching goal of eliminating TB in India by 2025, in alignment with the Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) target of eradicating the disease globally by 2030. [4]
Key Features and Benefits of the Nikshay Poshan Yojana
Some salient features and benefits of the Nikshay Poshan Yojana initiative launched by the Government of India include:
Eligibility
- All tuberculosis (TB) patients who have been notified on or after April 1st, 2018, as well as all existing TB patients undergoing treatment, are eligible to receive incentives.
- Eligibility for incentives is contingent upon the patient’s registration or notification on the NIKSHAY portal.
- The scheme is registered under the Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) system.
Incentive
- Cash: A financial incentive of ₹500 per month is provided to each TB patient who has been notified for the entire duration of their anti-TB treatment.
- In Kind: The provision of in-kind support ensures that the total value of the food basket provided to TB patients is at least ₹500 per month.
Each state has the authority to decide whether to offer the benefits in cash or in-kind, based on their discretion.
Application Process
- Patients are required to visit the nearest healthcare facility in order to enrol on the NIKSHAY portal.
- The necessary documents include bank details (either the patient’s own or those of a parent or guardian if the patient does not have a bank account) and an Aadhaar number. [5]
Revisions made in the Nikshay Poshan Yojana for timely TB Treatment support
To improve implementation efficiency and address challenges like delays, loss to follow-up, and resource optimization, modifications have been made to the benefits offered via the Nikshay portal. Initially, patients will receive INR 1500 at diagnosis instead of the previous INR 1000, followed by another INR 1500 after 84 days of treatment initiation. Subsequently, patients will receive a monthly benefit of INR 500.
The revised benefit system will be applicable to patients who are notified after January 1, 2024. Existing patients will continue to receive benefits according to the current frequency. [6]
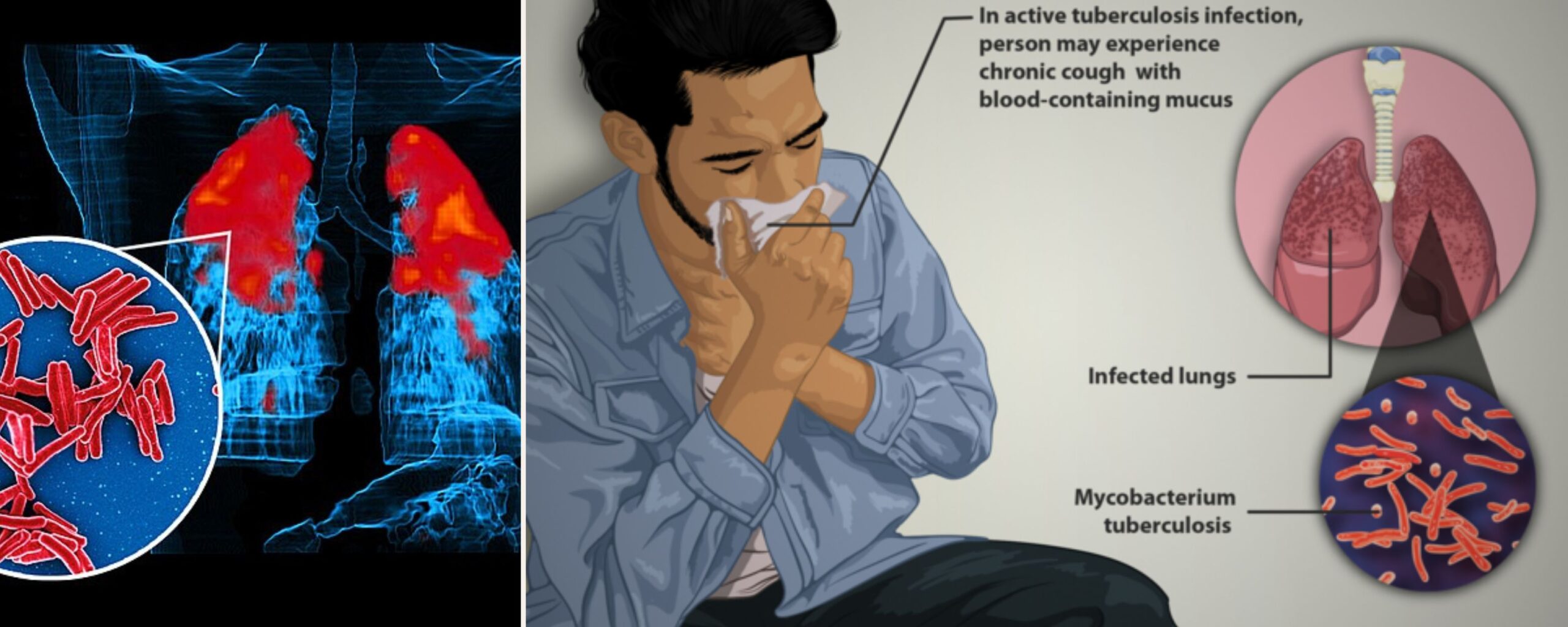
Impact and Challenges of the Nikshay Poshan Yojana
Since its inception, the Nikshay Poshan Yojana has made significant strides in addressing the nutritional needs of TB patients across India. By providing financial assistance for nutritious food, the scheme has helped alleviate the burden of malnutrition among TB patients and improve their treatment adherence.
Numerous challenges were identified in the Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) system for both healthcare providers and patients, including issues such as the absence of bank accounts and unlinked bank accounts. Lack of communication, stigma, low literacy rates, and the complex multi-step approval process were identified as significant obstacles. Furthermore, challenges persist in ensuring timely disbursement of financial assistance, reaching remote and marginalized communities, and sustaining long-term nutritional support for TB patients. Addressing these challenges requires continued commitment from government authorities, healthcare providers, and community stakeholders.
Conclusion
The Nikshay Poshan Yojana stands as a testament to India’s commitment to combating tuberculosis and promoting the health and well-being of its citizens. By recognizing the importance of nutrition in TB care and providing financial assistance for nutritious food, the scheme offers a holistic approach to TB treatment that addresses the multifaceted needs of patients. As efforts to eliminate TB intensify, initiatives like the Nikshay Poshan Yojana play a crucial role in ensuring equitable access to quality healthcare and fostering a healthier future for all.
- The prevalence of tuberculosis infection in India: A systematic review and meta-analysis - PMC (nih.gov)
- Press Information Bureau (pib.gov.in)
- https://pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=1975724
- 6851513623Nutrition support DBT Scheme details.pdf (tbcindia.gov.in)
- Nikshay Poshan Yojana (Nutritional Support To TB Patients) (myscheme.gov.in)
- Nikshay

Author: Dr. Anjali Singh
Subscribe to our Newsletter
Get Articles of your preference delivered to your Mailbox!