February: The Month of Gallbladder and Bile Duct Cancer Awareness
Introduction:
Gallbladder and bile duct cancer, though relatively rare, are fatal adversaries in the realm of oncology. February is observed as Gallbladder and Bile Duct Cancer Awareness Month. It is a global initiative to raise awareness about these organs and the rare but fatal malignancies associated with them. [1]
Understanding their nuances, risk factors, symptoms, and available treatments is imperative in fostering early detection and improving outcomes for those affected by these diseases.
Gallbladder and Bile Duct: A small organ with significant responsibilities
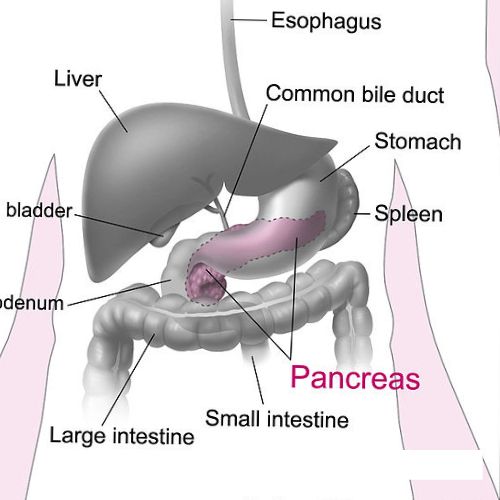
The gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ located beneath the liver in the upper right part of the abdomen.
- Its primary function is to store and concentrate the bile, a yellowish-green digestive fluid produced by the liver.
- Upon eating, the gallbladder releases bile into the small intestine to facilitate the digestion and absorption of fats.
- The bile ducts are small tubular structures that transport bile produced by the liver to the gall bladder and duodenum of the small intestine.
Gallbladder cancer begins in the innermost layers of the gallbladder and can subsequently spread to nearby tissues.
- Detecting this cancer can be difficult, primarily due to the small size of the gallbladder, which is mostly concealed by the liver.
- Bile duct cancer, also known as cholangiocarcinoma, can occur in any part of the biliary duct system, which includes the intrahepatic bile ducts within the liver and the extrahepatic bile ducts outside the liver. [2, 3]
The Prevalence and Importance
Gallbladder and bile duct cancers collectively represent a small percentage of all cancer diagnoses. However, their impact can be devastating due to late detection and limited treatment options.
Globally, gallbladder cancer ranks as the 23rd most common cancer. It is the 23rd most prevalent cancer in males and the 20th most common cancer in women. In 2020, there were more than 115,000 newly diagnosed cases of gallbladder cancer worldwide. India experiences a high prevalence of gallbladder cancer (GBC), contributing to roughly 10% of the global burden of GBC. Despite advancements in medical science, the survival rates for these cancers remain low, underscoring the urgent need for heightened awareness and research efforts. [4, 5]
Causes and Risk Factors of Gallbladder and Bile Duct Cancer
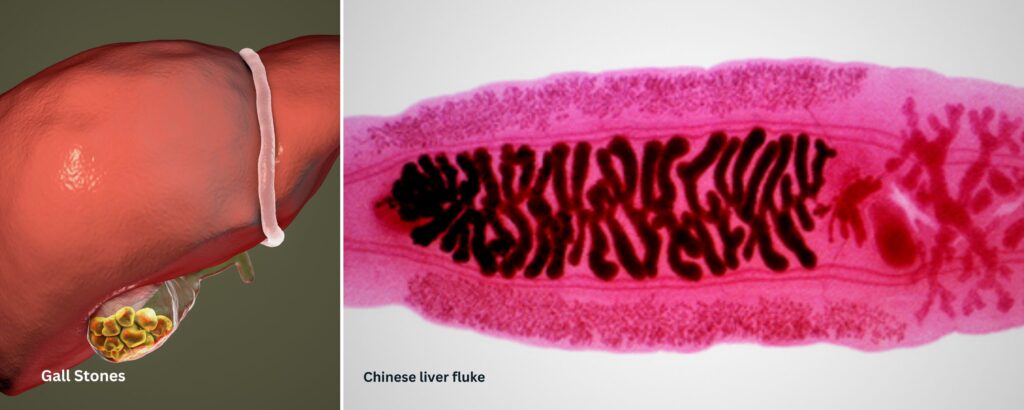
Though the precise origins of gallbladder cancer remain uncertain and unknown, mutations in gallbladder cells are widely acknowledged as a primary cause. Additionally, a prior history of gallstones is recognized as the primary risk factor for gallbladder cancer. These small, solid crystals, consisting of hardened bile and cholesterol, have the potential to develop within the gallbladder and impede bile flow, leading to discomfort, inflammation, and jaundice. It’s important to note that while gallstones elevate the risk of gallbladder cancer, the condition itself is relatively uncommon despite the widespread occurrence of gallstones.
Some common factors that increase the risk of developing gallbladder and bile duct cancer include:
- Gallstones: Individuals with a history of gallstones are at an elevated risk of developing gallbladder cancer.
- Age and gender: These cancers tend to occur more frequently in older individuals, with the risk increasing with age. Additionally, women are more likely to develop gallbladder cancer than men.
- Ethnicity: Certain ethnic groups, such as Native Americans and Mexican- Americans, have a higher incidence of gallbladder cancer.
- Gallbladder diseases and infections: Chronic inflammatory conditions (chronic ulcerative colitis), infections (Chinese liver fluke parasite infection), polyps, and cysts (bile duct cysts) are other gallbladder diseases that might raise the risk of gallbladder and bile duct cancer.
- Inflammation of bile ducts: Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PCS), characterized by inflammation of the bile ducts that carry bile from the liver and gallbladder, raises the risk of developing gallbladder cancer.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese increases the risk of developing gallbladder and bile duct cancer. [3, 6, 7, 8]
Symptoms of Gallbladder and Bile Duct Cancer
The signs and symptoms of gallbladder and bile duct cancer can be nonspecific and often mimic other gastrointestinal conditions. However, paying attention to the following warning signs is crucial.
Some of the common signs and symptoms of these cancers include:
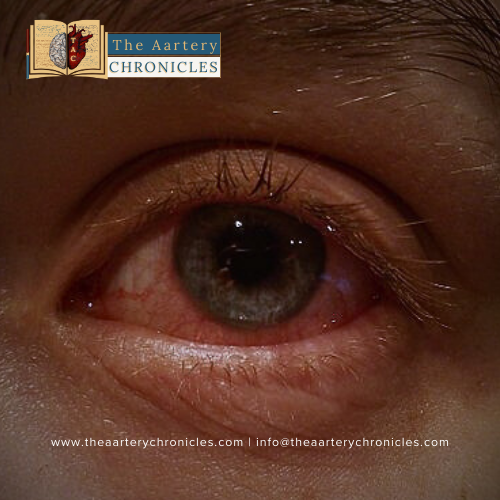
- Yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice)
- Dark urine and clay-coloured stool
- Abdominal Pain
- Unexplained weight loss
- Nausea and vomiting
- Abdominal bloating
- Lumps in the abdomen
- Fever [3,6]
Early detection is crucial for effective treatment
Detecting gallbladder cancer early is challenging yet crucial for effective treatment, as symptoms typically emerge only after the disease has advanced. Early detection remains the cornerstone of improving outcomes for gallbladder and bile duct cancer patients. Physicians typically begin by conducting liver function tests (LFT) to identify elevated levels of bilirubin. Various imaging techniques, such as abdominal and endoscopic ultrasounds, CT scans, and MRI scans, aid in the diagnosis of gallbladder and bile duct cancer.
Physicians utilize a staging system, known as the TNM system, to characterize the progression of gallbladder cancer. The TNM staging system comprises three essential components:
- T signifies the extent of tumour growth within the primary wall of the gallbladder.
- N indicates whether the cancer has metastasized (spread) to nearby lymph nodes.
- M denotes the presence or absence of cancer spreading to other organs. The liver, abdominal cavity lining, and lungs are frequently affected sites of gallbladder cancer metastasis. [7, 8]
Medical Management and Treatment for Gallbladder and Bile Duct Cancer
The medical management and treatment of cancers vary depending on the stage and type of cancer. A typical treatment approach encompasses a combination of surgical intervention, chemotherapy, and radiotherapy. In cases of early-stage cancers, the goal is the complete removal of the cancer to prevent its recurrence. In more advanced stages, treatment aims to prolong life expectancy and alleviate symptoms.
Gallbladder cancer treatment typically involves cholecystectomy, which is the surgical removal of the gallbladder. Additionally, radiation therapy is used to target and destroy cancer cells while slowing tumor growth, and chemotherapy involves the use of medications to fight against cancer cells. These treatments are frequently utilized in combination for effective management of the disease.
Key to a Healthy Lifestyle
- Consuming a nutritious diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins while minimizing processed foods and sugary drinks.
- Regular physical activity is essential, aiming for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous activity each week.
- Prioritizing sufficient sleep, typically 7-9 hours per night for adults, is crucial for overall health and well-being.
- Maintaining a healthy weight lowers the risk of developing serious health conditions like gallbladder and bile duct cancer.
- Managing stress through relaxation techniques, mindfulness, or hobbies can also contribute to a healthier lifestyle.
- By avoiding smoking and excessive drinking, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing serious health conditions and improve their overall quality of life.
- Getting vaccinated against the hepatitis B virus (HBV) to prevent liver and gallbladder infections.
How Can You Get Involved?
During Gallbladder and Bile Duct Cancer Awareness Month, there are several ways you can get involved in raising awareness and supporting individuals affected by these cancers:
- Educate Yourself and Others: Learn about the risk factors, symptoms, and treatment options for gallbladder and bile duct cancer, and share this information with your friends, family, and community.
- Advocate for Early Detection: Encourage individuals to listen to their bodies, pay attention to potential symptoms, and seek medical attention promptly if they have any concerns.
- Support Research Efforts: Consider donating to organizations and research institutions dedicated to advancing the understanding and treatment of gallbladder and bile duct cancer.
- Provide Support: Offer support and encouragement to individuals diagnosed with gallbladder and bile duct cancer and their loved ones, whether through emotional support, practical assistance, or connecting them with resources and support networks. [1]
Conclusion
As we observe Gallbladder and Bile Duct Cancer Awareness Month this February, let us unite in our efforts to educate, advocate for, and support those affected by these often-overlooked malignancies. By promoting awareness, fostering early detection, and advancing research, we can strive towards better outcomes and improved quality of life for individuals battling gallbladder and bile duct cancers. Together, we can make a difference in the fight against these diseases.
- February is Gallbladder and Bile Duct Cancer Awareness Month. News » Pancare Foundation
- Gallbladder and Bile Duct Cancer Awareness Month | The AACR
- Gallbladder & Bile Duct Cancer Awareness Month Is Observed in February | Moffitt
- Gallbladder cancer statistics | World Cancer Research Fund International (wcrf.org)
- Epidemiology of gallbladder cancer in India - Dutta - Chinese Clinical Oncology (amegroups.org)
- Gallbladder & Bile Duct Cancer Awareness: Signs & Risk Factors - NFCR
- Gallbladder Cancer: Symptoms, Treatment & Prognosis (clevelandclinic.org)
- Cholangiocarcinoma (Bile Duct Cancer): Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment (clevelandclinic.org)

Author: Dr. Anjali Singh
BDS [KGMC, Lucknow]
- Medicine
- Nutrition And Diet