Twin Pregnancy: Types, Risks, Diet, and Care for a Healthy Journey
Hearing news about a twin pregnancy often brings double the joy and excitement. As the saying goes, “Double the joy, double the jitters,” it’s a moment that lights up smiles but also brings unique challenges and responsibilities. Carrying two fetuses in the womb is a remarkable experience, often accompanied by heightened medical attention and care.
Did you know that one of the earliest mentions of twins dates back thousands of years? The Bible refers to Jacob and Esau, fraternal twins born around 1990 BC. Their story is one of many that highlights the historical fascination with twins.
In this article, we’ll explore the fascinating world of twin pregnancies, delving into their unique characteristics, the joys they bring, and the challenges they pose. Let’s discover the beauty and wonder of this incredible phenomenon together!
What is Twin Pregnancy?
A twin pregnancy occurs when two fetuses develop in the uterus simultaneously, resulting in the birth of twins. Depending on how the twins are formed, they are classified into two main types:
Monozygotic (Identical) Twins
- Monozygotic twins develop from a single fertilized egg that splits into two embryos.
- They are always of the same sex and share identical genetic makeup.
- Have the same HLA typing (Human Leukocyte Antigen typing, a test used to identify proteins on cells that regulate immune responses and compatibility).
Dizygotic (Fraternal) Twins
- Dizygotic twins develop from two separate eggs fertilized by two different sperm cells.
- They may be of the same or opposite sexes.
- Possess unique genetic and physical traits, similar to any two siblings born at different times.
Key Fact: Monozygotic twins are relatively rare compared to dizygotic twins, with the latter being more common due to
- Genetic factors
- Maternal age
- Fertility treatments
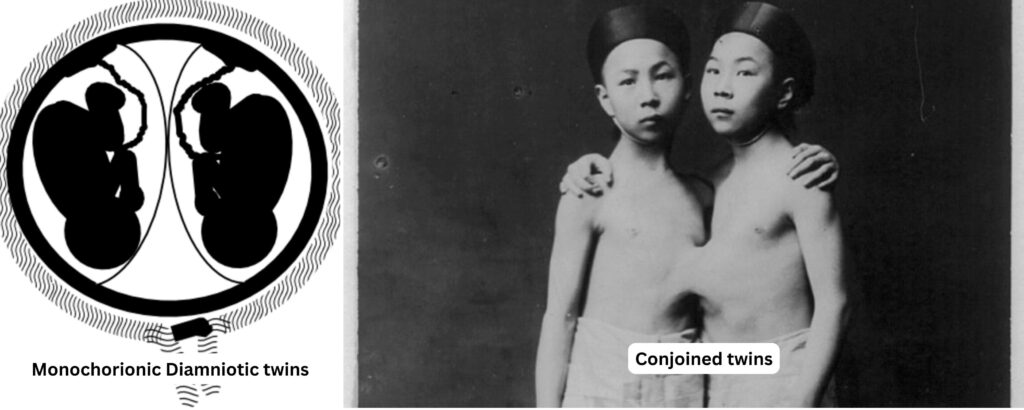
Types of Monozygotic Twins
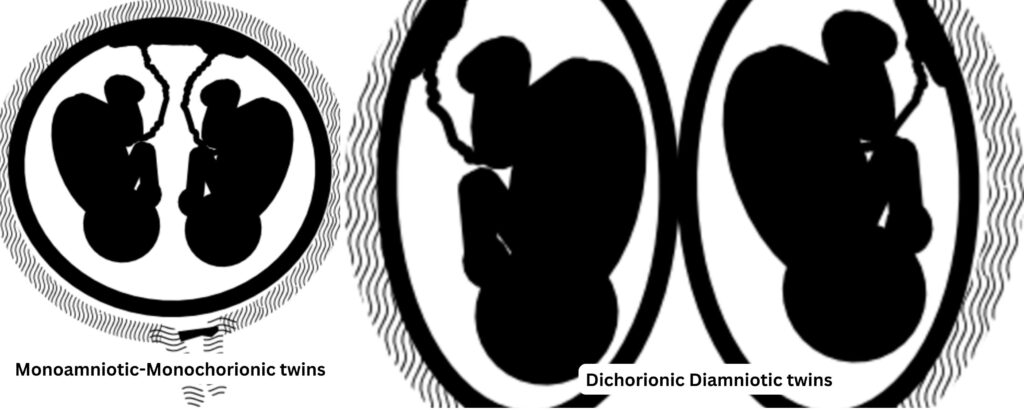
The type of monozygotic twins depends on when the fertilized egg splits:
- Within 72 hours: Diamniotic dichorionic twins (30%) (each twin has its own amniotic sac and placenta).
- 4–8 days: Diamniotic monochorionic twins (66%) (twins share a placenta but have separate amniotic sacs).
- >8 days: Monoamniotic monochorionic twins (3%) (twins share both the placenta and the amniotic sac).
- >13 days: Conjoined twins (<1%) (twins are physically connected due to incomplete splitting of the embryo).
How Common Are Twins? The Fascinating Stats!
• Identical Twins (Monozygotic): A rare phenomenon, happening in just 1 in 250 pregnancies across the globe.
• Fraternal Twins (Dizygotic): More frequent and fascinating, occurring in about 1 in 80 pregnancies worldwide.
Fun Fact: Dizygotic twins are influenced by genetics, age, and even dietary factors—making them a unique blend of nature and nurture!
Symptoms and Signs of Twin Pregnancy
Twin pregnancies share many symptoms with singleton pregnancies, though they are often more pronounced:
Symptoms
• Breast tenderness
• Fatigue
• Frequent urination
• Increased appetite
• Morning sickness
Signs
• Early fetal movements
• Heightened uterine size compared to gestational age
• Higher-than-average weight gain
• Elevated levels of hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) and AFP (alpha-fetoprotein)
Fascinating Phenomena in Twin Pregnancies
Superfecundation
A rare and intriguing event where two ova released during the same menstrual cycle are fertilized by sperm from separate acts of intercourse, resulting in twins with different genetic fathers.
The movie Bad News, directed by Anand Tiwari, highlights the concept of superfecundation in detail, raising awareness among the general public.
Superfetation
An even rarer phenomenon where two ova from different menstrual cycles are fertilized and develop simultaneously, leading to twins conceived at other times but born together.
Fun Fact: These phenomena are so unusual that they often make headlines when discovered!
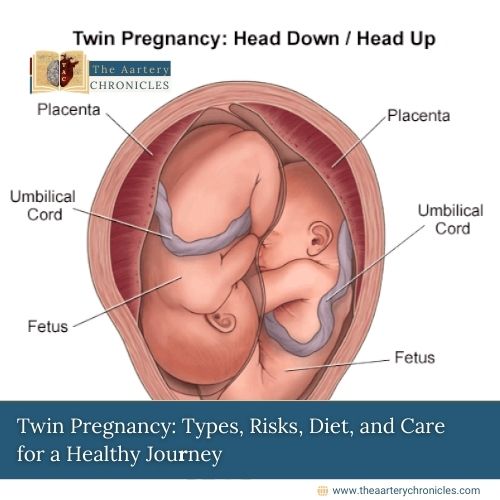
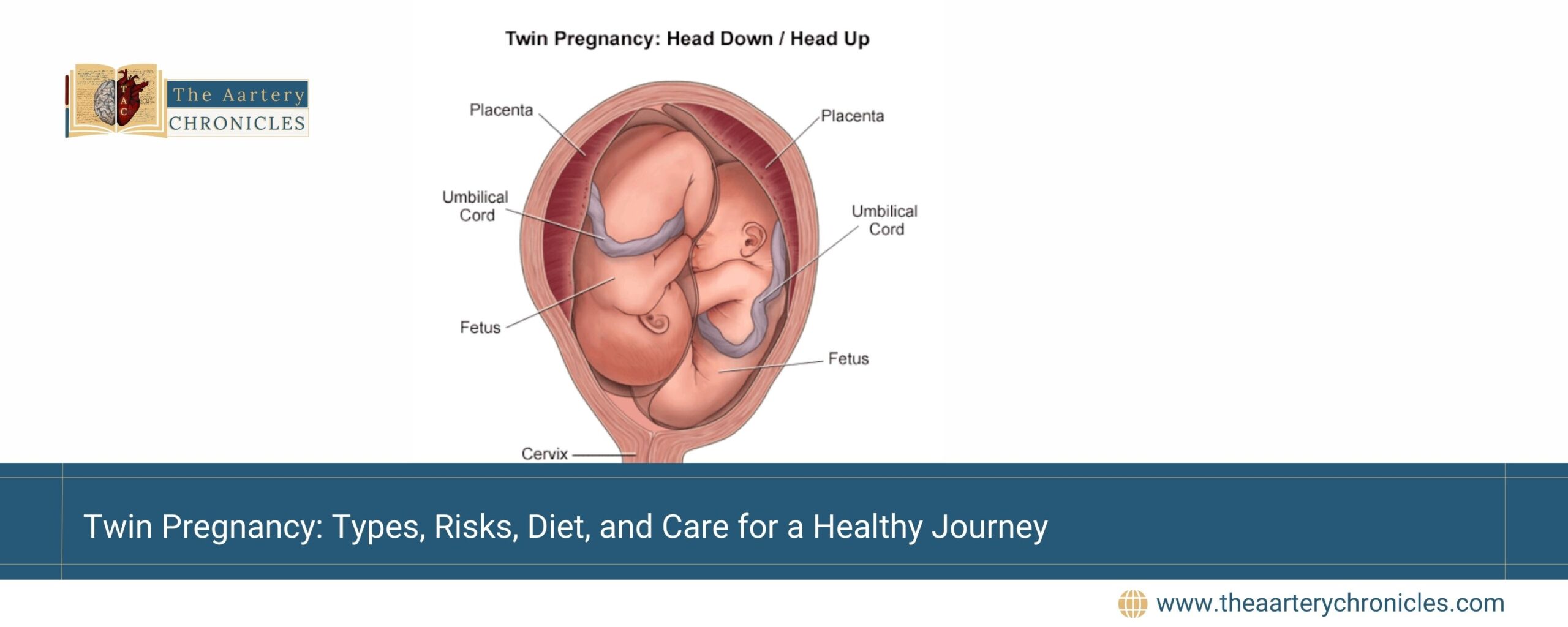
Twin Presentation: Understanding Fetal Positions for Delivery Planning
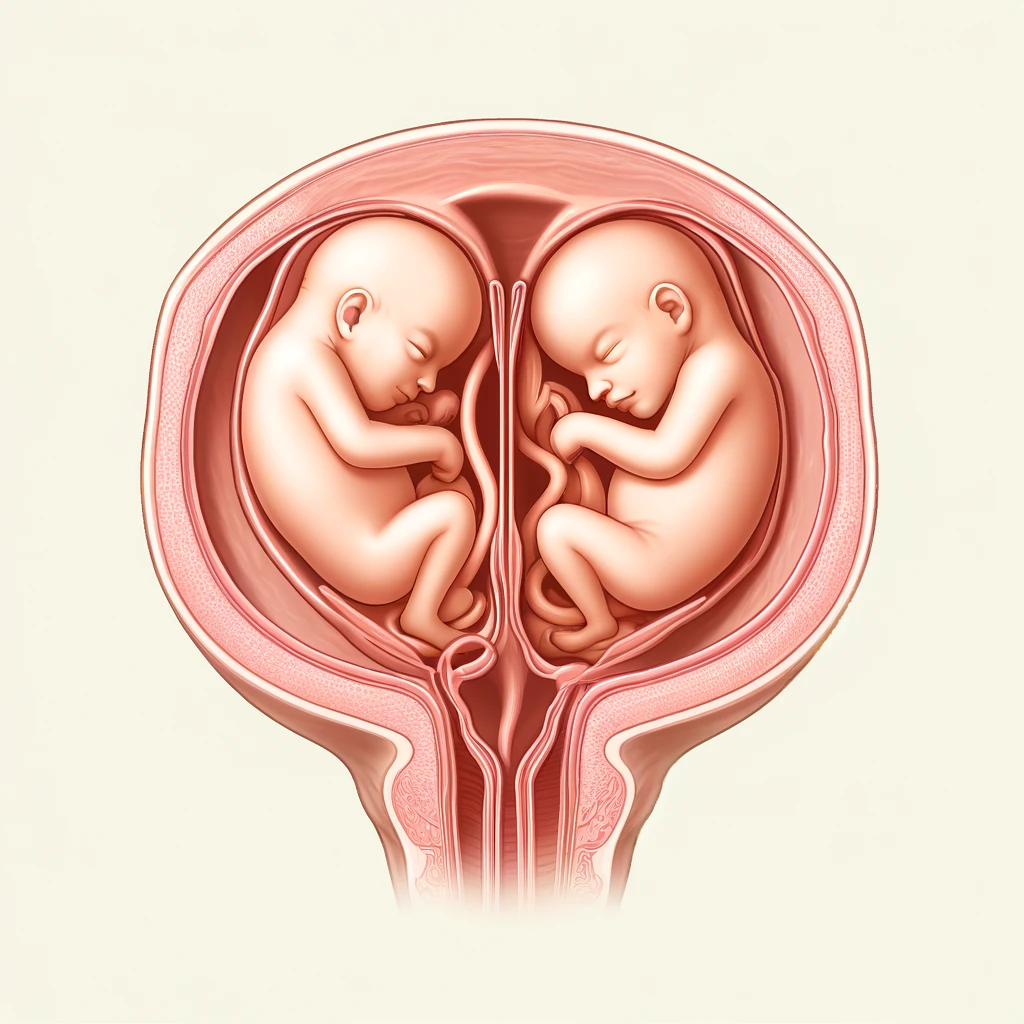
The position of twins in the uterus can vary, and understanding their presentation is crucial for planning delivery:
1. Both heads down (50%) — The most common and ideal position for vaginal delivery.
2. First twin vertex, second breech (30%) — The first twin is head-down, while the second is bottom-first.
3. First breech, second vertex (10%) — The first twin is breech, and the second is head-down.
4. Both breech (10%) — Both twins are positioned bottom-first.
5. First vertex, second transverse (rare) — The first twin is head-down, and the second lies sideways.
6. Both transverse (very rare) — Both twins lie sideways, presenting challenges for delivery
The position of the twins can significantly impact the method of delivery, whether vaginal or cesarean!
Key Ultrasound Signs for Determining Twin Chorionicity
- Twin Peak Sign (Lambda Sign): This triangular appearance of the chorion between the intertwin membrane indicates dichorionic twins and is typically observed between 10-14 weeks of pregnancy.
- T Sign: The absence of the Twin Peak Sign, where no chorion extends between the intertwin membrane, indicates monochorionic twins.
Did You Know? These signs help determine whether the twins share a placenta and the potential risks associated with their development!
Risk Factors for Twin Pregnancy
Several factors can increase the likelihood of a twin pregnancy:
- Maternal Age: Women over the age of 35 are more likely to conceive twins due to hormonal changes that increase the chance of releasing multiple eggs.
- Personal History: A maternal history of twins, especially fraternal twins, can significantly increase the chances of having twins.
- Fertility Treatments: Certain fertility procedures have been linked to higher twin pregnancy rates, such as
- IVF (In Vitro Fertilization)
- ICSI (Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection)
- Previous High-Risk Pregnancy: Women with a history of high-risk pregnancies, may be more likely to conceive twins again like:
- Ectopic pregnancies
- Prior twin pregnancies
- Obesity: A BMI (Body Mass Index) above 30 can elevate the odds of having a twin pregnancy, possibly due to hormonal factors influencing ovulation.
Interesting Insight: With advances in fertility treatments, more women are conceiving twins, making it important to monitor and manage risks closely during pregnancy.
Complications Associated with Twin Pregnancy
Maternal Complications
Twin pregnancies carry a higher risk of certain complications for the mother, including:
- Postpartum Hemorrhage (PPH): Increased risk of heavy bleeding after delivery.
- Anemia: Due to the increased blood volume and demands of carrying two fetuses, anemia is more common.
- Hypertension (PIH): Pregnancy-induced hypertension, which can lead to preeclampsia, is more prevalent.
- Hyperemesis: Severe morning sickness or nausea and vomiting during pregnancy.
- Gestational Diabetes: Increased risk of developing diabetes during pregnancy, which can affect both mother and baby.
- Preterm Labor: Twin pregnancies are more likely to result in early labor and delivery.
Fetal Complications
The risks for the babies can also be higher in twin pregnancies:
- Prematurity: The most common complication, as twin pregnancies often result in preterm births.
- Twin-to-Twin Transfusion Syndrome (TTTS): A condition where one twin receives more blood supply than the other, leading to complications for both.
- Intrauterine Growth Restriction (IUGR): One or both twins may not grow properly due to insufficient nutrients and oxygen.
- Congenital Anomalies: Increased risk of birth defects or developmental issues in one or both fetuses.
- Fetal Demise: A higher risk of one or both babies not surviving to full term.
Diagnosing Twin Pregnancy
The diagnosis of a twin pregnancy is most commonly made through ultrasound, which is considered the gold standard.
- It is typically confirmed around the 10th week of pregnancy.
- Ultrasound allows doctors to visualize the number of fetuses and their positioning within the uterus.
Doppler Ultrasound is often used for further assessment, especially in identifying potential complications like Twin-to-Twin Transfusion Syndrome (TTTS), a condition that can significantly affect the health of both babies.
- Doppler ultrasound helps in evaluating blood flow between the twins, providing valuable information about their condition.
Managing Twin Pregnancy
Managing twin pregnancies requires close monitoring and specialized care to ensure the health and safety of both the mother and the babies. Depending on the circumstances, different delivery methods may be considered:
- Natural Vaginal Delivery (NVD): This is the preferred method if both twins are in favorable positions, typically with one twin head-down and the other in a manageable position.
- Cesarean Section (C-section): Often recommended when complications arise, such as
- Abnormal fetal positioning
- Fetal distress
- The first twin being in a breech or transverse position
- Internal or External Podalic Version: These techniques may be employed under general anesthesia to reposition the second twin if it is not in an ideal position for delivery.
Twin pregnancies often involve a higher level of monitoring throughout the pregnancy and during delivery to manage any potential complications effectively.
Dietary Recommendations for Twin Pregnancy
A balanced, nutrient-dense diet is essential for the health and well-being of both the mother and her growing twins.

Here are some key dietary recommendations for Twin Pregnancy:
- Eat a Variety of Nutrient-Rich Foods: Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy to ensure all essential nutrients are met.
- Focus on Key Nutrients: Prioritize foods rich in protein, calcium, iron, folate, and omega-3 fatty acids. Good options include salmon, eggs, leafy greens, legumes, and fortified cereals.
- Limit Unhealthy Foods: Avoid processed foods, excessive salt, and sugary drinks, as they can contribute to unnecessary weight gain and increase the risk of complications.
Proper nutrition is vital during a twin pregnancy to support both the mother’s increased energy needs and the babies’ rapid growth and development.
Pros and Cons of Twin Pregnancies
Twin pregnancies offer unique joys but also come with heightened challenges, making it crucial for expectant mothers to receive proper care and support.
Advantages
- Double the Joy: The experience of raising two babies simultaneously can bring immense happiness, with siblings sharing milestones, creating a unique bond.
- A Blessing for those with Infertility: Twin pregnancies can be a miracle for couples who have struggled with infertility or have undergone fertility treatments, offering a chance to have two children at once
Disadvantages
- Increased Health Risks: Twin pregnancies carry a higher risk of maternal and fetal complications, including
- Preterm labor
- Gestational diabetes
- Hypertension
- Greater Demands on the Mother: Both physical and emotional strains are heightened, with
- Increased fatigue
- Enhanced emotional stress
- A greater need for support throughout the pregnancy
Conclusion
Carrying twins is a beautiful yet demanding journey that requires resilience, proper care, and plenty of support. To all the incredible mothers out there, your strength in nurturing two lives simultaneously is truly awe-inspiring. Remember, every twin pregnancy is unique, and consulting with your healthcare provider for personalized guidance and advice is essential to ensure a healthy and joyful experience for both you and your babies. “With the right care, you can manage this extraordinary chapter with confidence and grace.”
- Twin Pregnancy – Cleveland Clinic | https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/23158-twin-pregnancy
- Williams Obstetrics, 24th Edition
- Novak’s Gynecology, 15th Edition
- Dutta’s Obstetrics &Gynecology, 8th Edition
- Shaw’s Gynecology, 16th Edition

TAC Desk
Reviewed By: Dr Aarti Nehra








