Understanding Female Infertility: Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatments
Introduction
Infertility is a deeply personal and often challenging experience for couples trying to conceive. Defined as the inability to achieve pregnancy after one year of unprotected intercourse, infertility affects millions worldwide. While it can stem from either partner, female factors contribute to nearly half of all cases.
Before diving into the causes and treatments, let’s understand the prevalence of infertility:
Relative Prevalence of Infertility Causes
The prevalence of infertility causes can provide clarity and facilitate diagnostic assessment. Here’s a breakdown of the contributing factors:
- Male factors: 25-40%
- Female factors: 40-50%
- Both partners: 10%
- Unexplained: 10%
Causes of Female Infertility
Female infertility can arise from various factors, the most common being ovarian issues. Here are the primary contributors:
1.Cervical Factors
- Immunological causes: Sometimes, the immune system can produce antibodies that attack sperm, preventing successful fertilization.
2. Uterine Factors
- Tuberculosis (TB): Pelvic TB can cause scarring in the uterus, reducing fertility.
- Asherman Syndrome: This condition involves uterine scarring, often following surgeries or infections.
- Submucosal Fibroids: These benign growths within the uterus can interfere with embryo implantation.
- Congenital Malformations: Structural abnormalities in the uterus present from birth can hinder pregnancy.
- Müllerian Agenesis: A rare condition where the uterus and upper vaginal tract fail to develop.
3. . Ovarian Factors
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): A hormonal disorder that disrupts ovulation and is a leading cause of infertility.
4. Peritoneal Factors
- Endometriosis: A condition where uterine tissue grows outside the uterus, causing inflammation and impairing fertility.
Tests to Diagnose Female Infertility

Tubal Patency Tests:
- Hysterosalpingography: A radiological test performed in the early proliferative phase to assess the fallopian tubes.
- Laparoscopic Chromopertubation: The gold standard for detecting tubal blockages using methylene blue dye.
- Hysteroscopy: An advanced procedure to identify and treat intracavitary abnormalities.
Post-Coital Test: Evaluates sperm survival in cervical mucus after intercourse to pinpoint potential issues.
Other Investigations:
- Ultrasound (USG): Detects uterine abnormalities like fibroids or scarring.
- Sonohysterography: The saline solution is injected into the uterine cavity during a transvaginal ultrasound to provide detailed imaging.
- MRI Scan: Offers precise imaging for complex cases
Treatments for Female Infertility
Advances in medical science have made infertility treatable. Here are the common approaches:
1. Hormonal Therapy
- Clomiphene Citrate: A non-steroidal medication that stimulates ovulation by blocking estrogen receptors in the hypothalamus.
- Dosage: Typically, 50 mg is taken from day 2 to 6 of the menstrual cycle. The dose can be increased monthly up to 250 mg.
- Effectiveness: Ovulation usually occurs 5-7 days after the last dose, and therapy is recommended for up to six cycles.
- Human Menopausal Gonadotropin (HMG): Used to stimulate ovarian follicles when other treatments fail.
2. Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART):
- In Vitro Fertilization (IVF): The most effective fertility treatment, where eggs are fertilized in a lab and implanted into the uterus.
- Ideal for conditions like fallopian tube blockages, ovulation disorders, endometriosis, uterine fibroids, or previous surgeries.
- Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI): A single sperm is injected directly into an egg, often used for severe male infertility or failed IVF cycles.
- Intrauterine Insemination (IUI): Sperm is placed directly in the uterus around ovulation to increase the chances of fertilization
Key Points About IVF
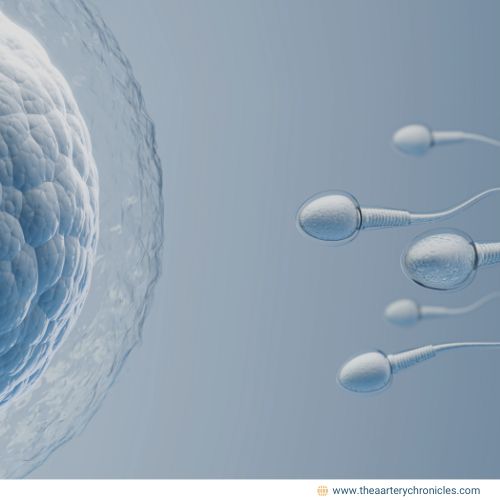
- What is IVF?
- It involves fertilizing eggs outside the body and implanting embryos into the uterus.
- A full cycle typically takes 2-3 weeks.
- Who benefits from IVF? Women over 40 or those with specific conditions like
- Fallopian tube damage
- Endometriosis
- Uterine fibroids
- Success rates: IVF is the leading assisted reproductive technology, offering hope to many couples
Lifestyle Tips to Improve Fertility
In addition to medical treatments, making lifestyle changes can significantly impact fertility:
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
- Reduce stress through mindfulness or exercise.
- Eat a balanced diet rich in antioxidants.
The Takeaway
Infertility, while challenging, is not insurmountable. Understanding its causes and exploring treatment options can empower couples on their journey to parenthood. If you’re facing difficulties conceiving, consult a specialist to identify the best course of action tailored to your needs.