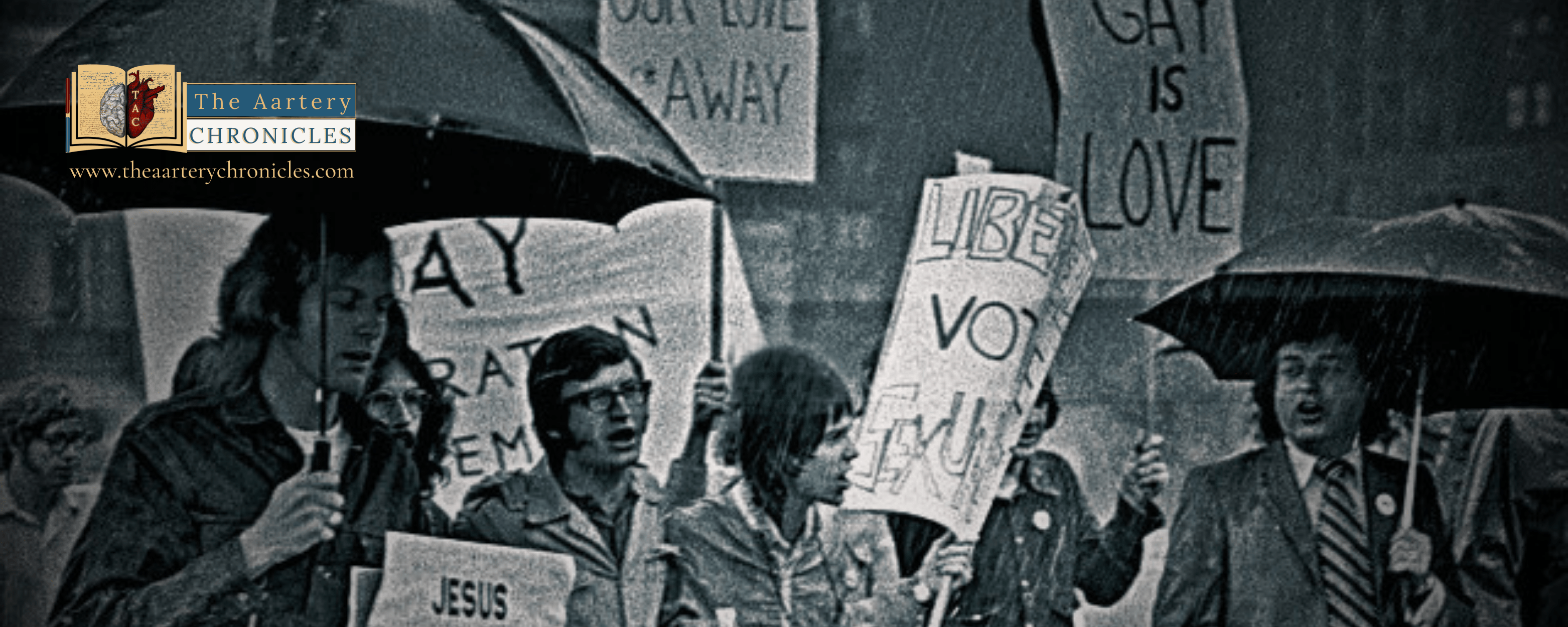
The Sex Spectrum: About Gender and Gender Dysphoria
Let’s talk about Sex, by sex, I mean “Gender”!
Biological sex is a primal aspect of human identity, encompassing physical and physiological characteristics that typically distinguish males and females. However, within this framework, the phenomenon of gender dysphoria arises, showcasing the intricate dance between biology and personal identity. This exploration seeks to shed light on the challenges accompanying gender dysphoria, underlining the crucial role of empathy in creating a more “inclusive society”… well at least theoretically.
"Gen V," the YA spinoff of "The Boys," introduces Jordan Li, a bi-gendered superhero played by London Thor and Derek Luh, challenging traditional gender norms. Jordan's unique ability to shapeshift between genders serves as a metaphor for the fluidity of gender identities, addressing acceptance and dysphoria issues. The character's struggle with societal expectations, particularly their father's disapproval, adds depth to the narrative, while the series breaks away from conventional superhero archetypes, representing a significant step forward in gender diversity within mainstream media. Despite being played by cis-gendered actors, Jordan avoids caricature and emerges as a powerful symbol of progress in representation, reshaping our preconceived ideas of what superheroes can look like.
Biological Sex and Intersex Variations:
Biological sex is traditionally classified into male and female, with primary and secondary sex characteristics (Hormones, Reproductive organs, Chromosomes, etc) differing between the two. Intersex conditions, such as Klinefelter Syndrome and Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome, demonstrate the complexity of sex variations beyond the binary model.
Individuals with Klinefelter Syndrome possess an extra X chromosome, leading to a chromosomal pattern of 47, XXY. This condition results in physical features such as tall stature, reduced muscle mass, and gynecomastia. Cognitive and behavioural challenges, including language delays and ADHD, may also be present. While Klinefelter Syndrome poses medical concerns, including infertility, hormone replacement therapy and fertility treatments can mitigate associated effects. A personal account from an individual with Klinefelter Syndrome underscores the complexity beyond the male-female dichotomy.
AIS involves insensitivity to androgens, causing individuals with XY chromosomes to develop along female lines. Despite male chromosomes, physical features such as breast development may occur. AIS highlights the complexity of biological sex determination and the influence of hormonal responsiveness. In these individuals, the testes typically remain in the abdominal or pelvic cavity instead of descending into the “Ball-sack” aka Scrotum.
CAH, an anatomical intersex condition, results in the overproduction of androgens, leading to the virilization of external genitalia in individuals with XX chromosomes. CAH presents how hormonal imbalances during development can impact physical characteristics.
“Living with Klinefelter Syndrome, I’ve learned that biological diversity is the norm. It’s time society recognises and embraces this reality.”
Reference: Intersex Society of North America
Transgender Identities and Gender Dysphoria
Transgender individuals experience a misalignment between their gender identity and the sex assigned at birth. It is crucial to distinguish between intersex and transgender, as the former pertains to biological variations, while the latter involves gender identity.
Gender dysphoria emerges when someone experiences distress due to the misalignment between their gender identity and assigned sex at birth. It’s crucial to approach this subject with empathy, recognising the psychological aspects contributing significantly to the challenges. As one individual shared, “Empathy is the bridge that connects us to the human experience of gender diversity.” This quote is a bit bizarre as the bridges burn and the things often fall apart! The quote is still inspiring!
Positive Aspects and Experiences: Optimism!
Amidst the challenges, stories of triumph and empowerment emerge. Personal narratives reveal individuals who, through self-acceptance and community support, have navigated the complexities of gender dysphoria successfully. High-profile examples, like Laverne Cox and Elliot Page, serve as powerful illustrations of resilience and success within the gender-diverse community.
“Empathy is the bridge that connects us to the human experience of gender diversity.”
Challenges and Concerns: Reality!
Despite these positive aspects, individuals with gender dysphoria face mental health challenges, heightened by discrimination and societal attitudes. Candid acknowledgement of these challenges is vital for creating a more inclusive society.
“By being true to myself, I hope to inspire others to embrace their authenticity and challenge societal norms.”
Reference: GLAAD – Laverne Cox
Healthcare Considerations:
Access to gender-affirming treatments and the role of healthcare professionals are crucial. Advocacy organizations like the World Professional Association for Transgender Health (WPATH) tirelessly work to promote transgender healthcare rights.
“Everyone deserves healthcare that respects their gender identity. It’s a basic human right.”
Reference: WPATH
Relationships and Social Dynamics:
Navigating relationships proves complex for those with gender dysphoria. Misunderstandings can strain familial and romantic relationships. Personal stories also reveal that love and acceptance can be powerful allies in the journey of gender self-discovery.
“Love knows no gender. Embracing diversity in relationships is a testament to the richness it brings to our lives.”
Reference: PFLAG
Education and Workplace Challenges:
Educational and workplace settings often become battlegrounds where discrimination poses significant obstacles.
“Educational institutions and workplaces must actively cultivate environments that celebrate diversity and inclusion.”
Reference: Human Rights Campaign
Promoting Mental Health:
Addressing mental health risks and self-harm concerns is paramount. Initiatives like The Trevor Project, providing mental health support to LGBTQ+ individuals, demonstrate the shared responsibility in promoting mental well-being.
“Empathy and support save lives. Together, we can create a world where mental health is a priority for all.”
Reference: The Trevor Project
Physical Health Considerations:
For some with gender dysphoria, medical interventions like hormone therapy or gender-affirming surgeries become part of their journey. Understanding the risks and benefits is crucial, highlighting the importance of informed decision-making. Ongoing medical research contributes to the evolving landscape of gender-affirming care.
“Informed decisions empower individuals to take control of their health. Comprehensive healthcare includes affirming gender diversity.”
Reference: American Medical Association
Conclusion:
In conclusion, acknowledging the challenges and triumphs of gender dysphoria is pivotal for creating a society that embraces diversity. As one quote aptly puts it, “In embracing diversity, we enrich the tapestry of humanity.” Understanding and empathy serve as catalysts for progress in gender diversity, propelling us towards a future where acceptance is the norm.
Regardless of how you identify—whether as male, female, a tree, or even a bunny—embracing and accepting yourself is crucial. Accept all the strengths and flaws, dark and light and only then expect others to accept you. Internal bias can have devastating effects and is often exploited by others. Make peace with yourself, and respect boundaries as we all have personal choices.
The images included in this content have been generated using artificial intelligence (AI) technology. These visuals are the result of computer algorithms and data processing, rather than traditional human photography or design. Please keep in mind that AI-generated images are subject to copyright and usage restrictions, as determined by the creators and organizations behind the AI algorithms.

Dr Darshit Patel, MD General Medicine