
Kleine-Levin Disease: All that You Need to Know
Summary: Kleine-Levin Disease (KLS) is a rare neurological sleep disorder marked by recurring episodes of extreme sleep lasting up to 20 hours a day, along with behavioral and cognitive changes. This article explains what KLS is, why it occurs, how it presents, how it is diagnosed, and how symptoms are managed despite the absence of a permanent cure.
Kleine-Levin Disease: Understanding a Rare Sleep Disorder
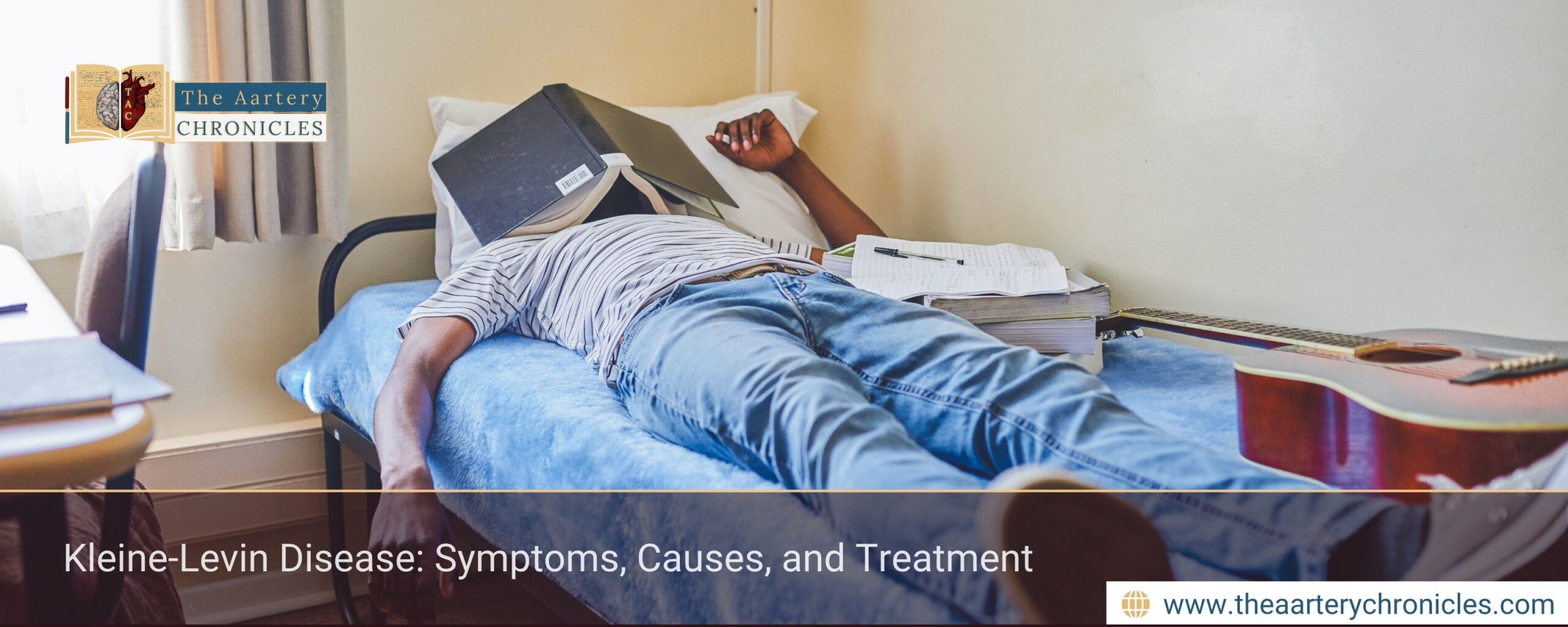
What if someone slept for nearly an entire day, 18 to 20 hours, yet still woke up exhausted?
Most adults need only 7–8 hours of sleep for restoration, but a rare neurological condition dramatically disrupts this balance. Kleine-Levin Disease, also known as Kleine-Levin Syndrome (KLS) or Sleeping Beauty Syndrome, is characterised by recurrent episodes of excessive sleep and altered behaviour.
This article aims to provide a clear, evidence-based overview of Kleine-Levin Disease, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment approaches, to help readers understand this uncommon but impactful disorder.
What Is Kleine-Levin Disease?
Kleine-Levin Disease (KLS) is a rare neurological disorder characterized by recurrent episodes of hypersomnia, during which individuals may sleep 18–20 hours per day or even longer. Along with excessive sleep, patients experience disturbances in behaviour, cognition, appetite, and mood.
Also referred to as Sleeping Beauty Syndrome, KLS most commonly affects adolescent males, although females can also be affected. During episodes, patients may appear confused, disoriented, or emotionally withdrawn when awake.
A defining feature of the disorder is its episodic nature. Between episodes, individuals typically return to completely normal functioning, showing no residual neurological or psychological symptoms. This intermittent pattern often contributes to delayed or missed diagnosis.
Did You Know?
“Kleine-Levin Syndrome (KLS) patients sleep for 18–20 hours a day and wake up only for basic biological functions such as eating, urinating, and defecating.”
Kleine-Levin Syndrome Causes
The exact cause of Kleine-Levin syndrome remains unknown, but several mechanisms have been proposed based on clinical observations. Possible contributing factors include:
- Hypothalamic dysfunction, as this brain region regulates sleep, appetite, and body temperature
- Post-infectious autoimmune responses, particularly following viral illnesses such as influenza
- Genetic or familial predisposition to neurological disorders
- Head injury or trauma affecting sleep-regulating brain centers
- Sudden hormonal changes, especially during adolescence
Despite these associations, no single cause explains all cases, reinforcing the complexity of this rare disorder.
Kleine-Levin Syndrome Symptoms
Also Read: Tears That Heal: How Crying Heals the Mind
Diagnosing KLS is challenging because symptoms may be subtle initially and can remain undetected for years. However, hallmark symptoms include:
- Extreme hypersomnia, often sleeping 18–20 hours per day
- Difficulty staying awake or performing routine daily activities
- Confusion, disorientation, or reduced awareness when awake
- Changes in appetite, including overeating or loss of appetite
- Mood disturbances, such as depression, anxiety, or irritability
- Social withdrawal and loss of interest in school, work, or daily routines
- Behavioural changes, including hallucinations or childlike behaviour
These symptoms typically occur in recurrent episodes lasting days to weeks.
Kleine-Levin Syndrome Diagnosis
There is no single definitive test for Kleine-Levin Disease. Diagnosis is primarily clinical and often delayed due to symptom overlap with psychiatric or sleep-related conditions.
A structured diagnostic approach includes:
- Detailed medical and sleep history, focusing on episodic hypersomnia
- Comprehensive neurological examination to exclude brain injury or disease
- Polysomnography (sleep study) to assess abnormal sleep patterns
- Brain imaging (MRI or CT scans) to rule out structural abnormalities
- Psychiatric evaluation to exclude mood or psychotic disorders
Did You Know?
KLS disease affects an estimated 1 to 5 people per million worldwide.
Kleine-Levin Syndrome Treatment
Currently, there is no permanent cure for Kleine-Levin Disease. Treatment focuses on symptom management and episode reduction. Common strategies include:
- Mood stabilizers and antidepressants to regulate mood and sleep-wake cycles
- Psychological support, including counseling or behavioral therapy
- Lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining consistent sleep routines and avoiding known triggers
- Family supervision and support, especially during active episodes, to ensure patient safety
Over time, many individuals experience a reduction in the frequency and severity of episodes, particularly as they age.
Currently, symptom control remains the primary approach, and spontaneous improvement is often observed over time.
Conclusion: Living With Kleine-Levin Disease
Kleine-Levin Disease (KLS) is a rare but manageable neurological sleep disorder that can significantly disrupt education, work, and social life. Because its causes are still not fully understood, delayed diagnosis is common, potentially prolonging patient distress.
Although no definitive cure exists, early recognition, supportive medical care, and strong emotional and family support can greatly improve outcomes. With time, most individuals gradually recover and regain a normal quality of life.
Awareness remains the most powerful tool for ensuring timely diagnosis, appropriate care, and better long-term outcomes for those affected by Kleine-Levin Syndrome.
Reference
- Cleveland Clinic. Kleine-Levin Syndrome.
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/23484-kleine-levin-syndrome#symptoms-and-causes - National Organization for Rare Disorders (NORD). Kleine-Levin Syndrome.
https://rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/kleine-levin-syndrome/
Dane
I am an MBBS graduate and a dedicated medical writer with a strong passion for deep research and psychology. I enjoy breaking down complex medical topics into engaging, easy-to-understand content, aiming to educate and inspire readers by exploring the fascinating connection between health, science, and the human mind.








