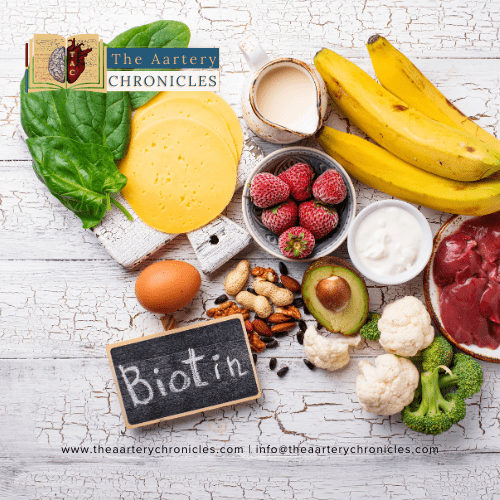
Reading Time: 5 minutes Biotin: Understanding Its Importance for Health and Well-Being The vitamin biotin, commonly referred to as vitamin B7 or vitamin H, is a water-soluble vitamin. The name “vitamin H” originates from the German words ‘Haar and Haut,’ which means hair and skin, highlighting its significance for these aspects of health. Biotin naturally occurs in various food items such as eggs, nuts and certain vegetables. It’s also commonly included in dietary supplements, often marketed for its potential benefits in promoting healthy hair and skin, as well as supporting overall well-being. The role of Biotin in our body: Biotin plays a vital role in the metabolism of fats, carbohydrates, proteins, etc. It helps convert these macronutrients into energy that the body can use. Also, biotin is responsible for maintaining cardiovascular health, and proper nerve functioning. Biotin is often associated with promoting the health of hair, nails, and skin. It is a common ingredient in many beauty supplements. Biotin is essential in the regulation of genes (as it modifies the activities of transcription factors), histone modifications, and cell signalling. Biotin is considered to be important in breaking down macronutrients, it is involved in processes such as the synthesis of fatty acids, breakdown of amino acids, and glucogenesis. Apart from this, biotin plays a key role in lactation, pregnancy, and regulation of blood sugar levels in type 2 diabetic patients. Sources of Biotin: Biotin is present in a variety of plant and animal-based food items, some of which include: Eggs: The egg yolk is particularly renowned for its high biotin content. However, it’s advisable to cook them as avidin in raw egg whites can interfere with biotin absorption. Spinach: Spinach is not only a good source of biotin but also offers a variety of other vitamins (such as Vitamin A, C, and Folic acid) and minerals (such as Iron, Calcium, and potassium). Sweet potatoes: Rich in antioxidants, fibre, vitamins, and minerals, sweet potatoes are a nutritious source of biotin Avocados: These are high in biotin and provide vitamin E, which is beneficial for skin and hair health. Organ meats: The liver, particularly chicken liver, is a potent source of biotin. Just 3 ounces of cooked chicken liver can provide a significant amount of biotin. Nuts: Nuts, such as almonds, peanuts, and walnuts, contain biotin and can be included in your diet. Along with these some other food items such as mushrooms, legumes, salmon, yeast, and dairy products are rich in biotin. What are the normal biotin levels? The normal ranges for biotin levels in the blood serum is approximately: Adults: 133-329 picomoles per litre (pmol/L) Children: 157-425 pmol/L On average in adults, the normal urine biotin concentration must be around 18-127 nmol/24hrs. Biotin Deficiency The biotin deficiency is relatively rare in healthy individuals because biotin is found in a variety of foods, and the body requires only a small amount of it. However, certain medical conditions or genetic factors can lead to biotin deficiency or impaired biotin metabolism. An unusual decrease in biotin excretion through urine signals a deficiency in biotin. Similarly, an elevated excretion of 3-hydroxyisovaleric acid (above 3.3 mmol/mol creatinine) or 3-hydroxyisovalerylcarnitine (above 0.06 mmol/mol creatinine) is indicative of reduced MCC (3-methylcrotonyl-CoA carboxylase) activity, suggesting a biotin deficiency. What are the signs and symptoms of Biotin deficiency? The Symptoms such as hair fall, conjunctivitis, brittle nails, and rashes, may indicate biotin deficiency. In severe cases of deficiency, In adults, symptoms may include seizures, skin infections, fragile nails, and neurological issues like depression, lethargy, hallucinations, and tingling sensations in the extremities. In infants, symptoms may manifest as hypotonia, lethargy, and developmental delays Serum concentrations of biotin and its metabolites can be increased by administration of oral doses. Recommended Amounts There’s no Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) for biotin because there isn’t sufficient evidence to determine a daily requirement for most healthy individuals. Adolescents and adults are often advised to take between 30 to 100 micrograms (mcg) of biotin daily. Supplements and gummies: The significance of biotin was first noticed when rats with the absence of biotin in their diet showed disorders such as neuromuscular dysfunction, dermatitis, and alopecia. In case suffering from a biotin deficiency, supplements can help level up the required concentrations of biotin in the body. A wide range of dietary supplements for biotin are available, including supplements that contain just biotin, and supplements containing various combinations of vitamins and B-complex. However, it is important to choose according to the individual’s deficiencies and requirements. Biotin gummies are a popular dietary supplement option for individuals looking to increase their biotin intake. Biotin gummies are easy to take and often more enjoyable than swallowing pills or capsules. Biotin for skin and hair health: In a recent decade, biotin has become commercially popular for its claimed benefits on skin, nails, and hair health. Biotin is an important nutrient that helps with the production of keratin. Hair Health: Studies reveal that low levels of biotin can cause hair loss. Biotin supplements are often prescribed for the strengthening of hair. Cosmetic products also tend to contain biotin as an alternative supplement. Biotin is known to improve the elasticity of hair and reduces brittleness which prevents the strands from breakage. It has been reported that people using biotin-enriched hair products experienced thickness in hair, texture, and overall hair health. Skin Health: Biotin is said to promote radiant complexion as it is significant in the production of fatty acids which are responsible for maintaining healthy skin cells. And speeds up the process of regeneration supporting the collagen protein which imparts elasticity to the skin. However, the complete role of biotin in maintaining healthy skin has not been elucidated by scientists. The influence of vitamins on the skin may be associated with the effect on the metabolism of fat. Despite the rising craze for biotin in the media, only a small amount of literature is found to support the biotin claims for skin and hair health. Conclusion: Biotin plays a vital role in