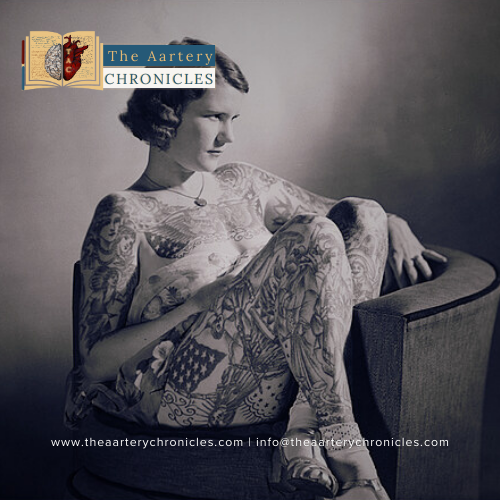
Reading Time: 6 minutes Ink and Introspection: Navigating the Art and Awareness of Tattoos Tattoo: An Imprint of Identity and History A Tattoo is referred to as a mark, an image, or a phrase that is intentionally and permanently fixed on the skin. This is usually done by a specific type of ink inserted into the epidermis of the skin. Throughout the annals of time, humanity has woven a narrative of skin-deep significance. For millennia, tattoos have been more than pigments; they are the brushstrokes of identity, a tableau of beliefs and emotions etched into the skin’s canvas. These indelible imprints, painstakingly embedded into the epidermal layers, evoke tales of status, convictions, love, embellishment, and sometimes even retribution. The origin of tattooing traces back through the ages, a window into cultures that have painted their stories across generations. A reflection of the human desire to etch one’s mark upon the world, tattoos have evolved from primitive tools to intricate designs woven with modern precision. They transcend the surface, weaving threads of heritage, forging connections with ancestral echoes, and resonating with the resonance of personal narratives. So, let us peer into the intricate designs that adorn the flesh, acknowledging the myriad reasons individuals bear these marks. The Earliest Testimony of Tattoos: Otzi the Iceman Among the annals of ancient history, one enigmatic figure stands as a frozen witness to the ancient art of tattooing. Europe’s famous mummy, Otzi or the Iceman was discovered in the Alps by German hikers in 1991. Approximately 5200 years ago, Otzi walked the rugged landscapes of Tyrol, leaving behind a legacy etched in ice and ink. After his death, the body and the tattoos were preserved in ice. Tattoos on the mummy were of ceremonial, religious, and ritualistic significance. The mummy was found to have 61 tattoos on the entire body. This frozen time capsule paints a vivid portrait of a world long gone. As we gaze upon the mummy adorned with symbols of yore, we find ourselves transported to an era of reverence and symbolism, where ink and skin harmoniously converged to inscribe stories of the human experience. Otzi’s legacy resonates as a captivating archaeological find and an invitation to peer into the lives of those who walked the Earth millennia ago. Far from mere adornments, his tattoos evoke a saga of rituals, connections, and echoes of beliefs that transcend time. In the ancient ink etched upon his skin, we encounter a bridge that unites us with our ancestors, a testament to humanity’s enduring curiosity and artistic expression. Mindset behind the Tattoo Culture: Earlier Beliefs Earlier the tattoos were not as much appreciated. Society still thinks of tattoos as a child’s non-traditional and rebellious mentality. Even today, in pockets of conservative thought, tattoos evoke associations with subcultures like gangsterism and mafia, reflecting a discord between ink and societal norms. Earlier Beliefs Earlier the tattoos were not as much appreciated. Society still thinks of tattoos as a child’s non-traditional and rebellious mentality. Even today, in pockets of conservative thought, tattoos evoke associations with subcultures like gangsterism and mafia, reflecting a discord between ink and societal norms. The Youth It can be seen that the tattoo culture is highly prevalent in today’s youth. There has been a rise in teenagers inking their bodies with permanent tattoos. With the “My life, my rules” motto of the current generation, teens find tattoos to be ‘happening’ and exclusive. The surging popularity of tattoos has ignited a revolution of colour, rendering these indelible marks more stunning and enchanting than ever before. The Youth It can be seen that the tattoo culture is highly prevalent in today’s youth. There has been a rise in teenagers inking their bodies with permanent tattoos. With the “My life, my rules” motto of the current generation, teens find tattoos to be ‘happening’ and exclusive. The surging popularity of tattoos has ignited a revolution of colour, rendering these indelible marks more stunning and enchanting than ever before. Personal Identity For many, the tattoo journey begins at the crossroads of trends and personal identity. The desire to align with the latest fashions or to cultivate an image of being “stud” or “cool” can spark an interest in body art. Most teenagers get inked just because of peer pressure without having any kind of awareness about the harmful impacts of permanently inking their bodies with tattoos. Personal Identity For many, the tattoo journey begins at the crossroads of trends and personal identity. The desire to align with the latest fashions or to cultivate an image of being “stud” or “cool” can spark an interest in body art. Most teenagers get inked just because of peer pressure without having any kind of awareness about the harmful impacts of permanently inking their bodies with tattoos. Health Risks Associated with Tattoos Within the realm of body art, a world of self-expression and transformation exists, intertwined with a web of health considerations that deserve our attention. Hepatitis Concerns: The unhygienic aspects of having a tattoo are often ignored by people. Alarming instances of hepatitis, particularly Hepatitis C, have emerged as a consequence of the growing popularity of tattoos. Chronic diseases like Hepatitis C can be transmitted through contact with contaminated blood. Tattoo parlours are home to many such life-threatening diseases. Increased Vulnerabilities to Infection: In the pursuit of the perfect design, it’s crucial to remember that improper care can quickly transform an artful expression into an infection-prone area. If tattoos are not meticulously cared for during the healing process, they can become sites of infection, leaving lasting scars—both physical and emotional. Infections of tattoos with bacteria particularly staphylococci that are known to be resistant to antibiotics can develop into chronic life-threatening sepsis. These skin infections from tattoos are mostly linked with Streptococcus pyogenes and Staphylococcus aureus. Ink Poisoning: In rare instances, an excess of ink can enter the bloodstream, leading to ink poisoning. This potentially life-threatening condition underscores the importance of choosing a reputable and professional tattoo artist who prioritizes safety. HIV Infection: HIV presents a distinct