Caution Advised: Alert Issued on Mefenamic Acid - What You need To Know
Mefenamic Acid: An Overview
Mefenamic acid, classified as a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), serves various medical purposes, including the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, dysmenorrhea, moderate pain, osteoarthritis, and dental pain
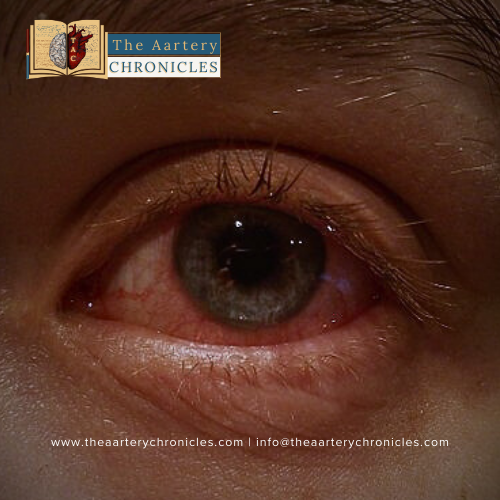
Recently, the Indian Pharmacopoeia Commission (IPC) issued a safety alert on November 30, 2023, regarding Meftal spas, a product containing mefenamic acid. According to reports, mefenamic acid has been associated with allergic reactions such as the Drug Rash with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS) syndrome, posing potential harm to internal organs.
Historical Background of Mefenamic Acid
Mefenamic acid was first synthesized in 1961 and it was introduced for pharmaceutical use in 1962. Parke, Davis, and Company, based in New Jersey, USA, marketed the drug primarily under the brand names Ponstan and Ponstel. In the years 1963 to 1967 the drug was approved in countries such as Germany, the UK, and the United States. In the 1980s, it became a generic medication and is now available worldwide under various brand names, including Meftal.
Mechanism of action of Mefenamic Acid
Prostaglandins are hormone-like substances responsible for causing inflammation, and the individual may experience pain and fever. Mefenamic acid reduces prostaglandin production by inhibiting COX-1 and COX-2, which are enzymes involved in prostaglandin synthesis. This reduction in prostaglandin levels leads to a temporary alleviation of pain and inflammation.
Side effects and Risks associated with Mefenamic Acid
Mefenamic acid may induce various side effects, including:
- Nausea
- Constipation
- Vomiting
- Dizziness
- Heartburn
- Diarrhea
- nervousness
- Headache
- Occasional rash and itching
- Tinnitus
- Loss of appetite
- Difficulty in urination
- Bloody stools and slowed breathing in case of overdose
Apart from these acute side effects, Studies suggest that people using mefenamic acid showed instances of liver injuries which may be caused by idiosyncratic hypersensitivity and the mechanism of action of mefenamic acid. Mefenamic acid has also been linked to elevated risks of heart strokes. Extended usage of mefenamic acid tablets has been associated with the risk of developing stomach ulcers, gut related complications.
DRESS Syndrome
DRESS (Drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms) has been observed in about 10% of people using mefenamic acid. The allergic reactions start appearing two or eight weeks after taking the drug. The DRESS syndrome can be fatal and is typically characterized by fever, rash, hematological abnormalities, and lymphadenopathy
Conclusion
Caution should be exercised in both the use and prescription of painkillers. Patients are strongly advised to consult a physician before using these medications. Healthcare professionals play a crucial role in emphasizing the need for cautious drug use to mitigate potential risks.
Author: Sanika Pande
- Medicine
- Nutrition And Diet
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.