FDA Warning: Smart Wearables and Blood Glucose Accuracy
Introduction
We are in an era where technology has become the most integral part of our lives. The advent of technology has also revolutionized the outlook on healthcare and wellness. Blood glucose monitoring is another such example of the shortcut and streamlined procedures thanks to the digital and technological progress that we have made.
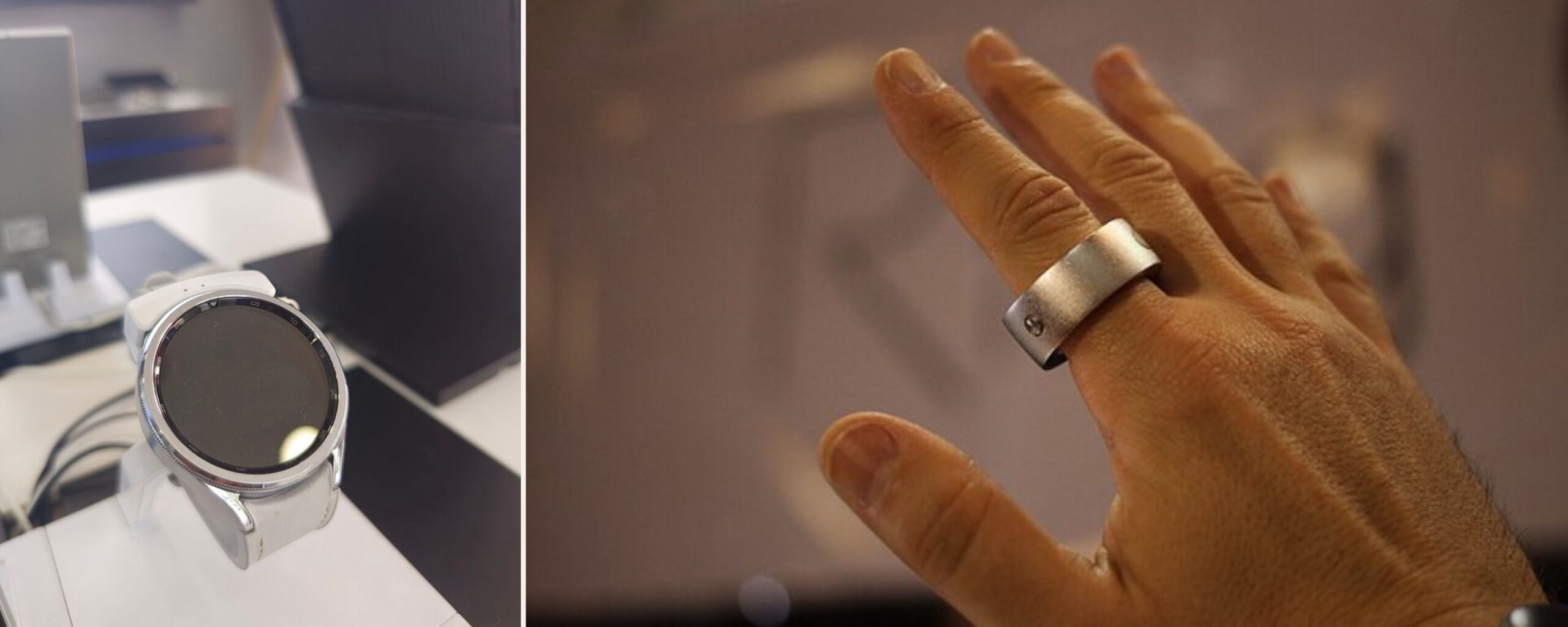
Lately, smartwatches and smart rings have become increasingly popular for monitoring health vitals. These claim to monitor blood glucose, heart rates, etc. Once the devices that merely showed the time today have become multifunctional devices that monitor health metrics.
However, it is important to consider if these wearables are reliable. Even if these devices offer real-time data and convenience, it is essential to be aware of the risks linked with depending solely on them for monitoring health vitals.
How do these devices work?
These devices primarily use non-invasive methods such as optical sensors for the measurement and do not test the blood for measuring blood glucose levels. Some smart rings and watches may use electrochemical sensors that help detect glucose in body fluids such as sweat.
The data collected through sensors is analyzed to provide real-time estimation of blood glucose levels. The readings of the blood glucose levels can be accessed on the device or the accompanied mobile applications.
The FDA warning
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued a warning for consumers, caregivers, and patients regarding the usage of smart wearables for monitoring blood glucose levels. The devices that claim to give readings of blood glucose levels without piercing the skin are distinct from the ones with FDA approval. FDA has not approved any smart wearable that claims to estimate blood glucose levels on its own.
For diabetic patients, inaccurate readings can disrupt managing the disorder. Critical errors such as taking the wrong dosage of insulin, and other medications including sulfonylureas can occur. These medications act quickly to reduce the level of blood glucose which may lead to coma, mental confusion, or death in the worst cases.

The regulatory actions of the FDA
The FDA has been routinely monitoring the market of medical devices and attained awareness of products being marketed without authorization. The agency has been making efforts to prevent the illegal promotion of smart devices by manufacturers and sellers claiming to measure levels of blood glucose.
Navigating the guidelines by the FDA
- Avoid buying unauthorized smart rings and smartwatches that claim to measure blood glucose
- Caution should be exercised regarding the safety and efficacy of the devices that have not been FDA-reviewed
- Consult a healthcare professional for an appropriate authorized device or an alternate way to measure blood glucose levels if the medical care is highly dependent on accurate measurements.
Conclusion
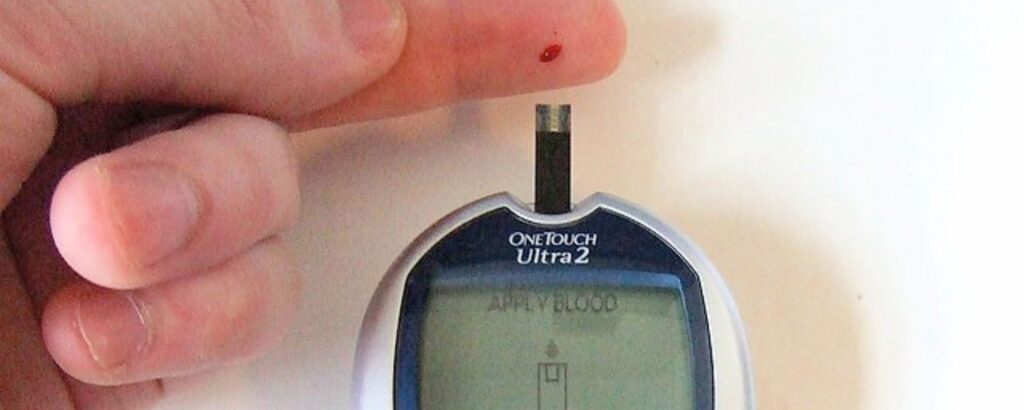
It is crucial to understand that smart wearables may not be able to replace the need for traditional blood glucose tests entirely. Blood glucose evaluation through traditional tests is essential for accuracy.
Another concern that can arise is the security and privacy of sensitive health data. With devices being linked to cloud services and mobile phone applications, the potential risk of unauthorized access to the data is inevitable. Furthermore, according to the FDA, any issue related to inaccurate blood glucose measurement from smart devices should be reported.
Source: Inputs from various media Sources
Sanika Pande
- Medicine and Diseases
- Nutrition and Diet