Summer Staples: The Distinctive Qualities of Curd and Yogurt
Overview
With the seasonal shift to summer, there has been a significant transition in the culinary preferences of the masses. People enjoy yogurt and curd, for its cold temperature and for the instant relief from the heat they provide.
The most popular summer staples have been consumed for centuries, particularly in warmer climates. Yogurt and curd have been used interchangeably in day-to-day lives however, they possess distinct characteristics which make them significantly different from one another.
Yogurt and curd differ from each other in the aspects of their production, nutritional profiles, microbial compositions, and sensory properties.
Methods of Production
The first and foremost difference between curd and yogurt is the distinct way both dairy delicacies are prepared.
Curd: Commonly known as Dahi is prepared by the method commonly known as coagulation. Milk is coagulated typically using lemon juice and vinegar. Pasteurized or boiled milk is soured using lactic acid bacteria
Lactic acid bacteria grow and multiply using the lactose in milk and form lactic acid. Some other strains may use citric acid, producing volatile organic chemicals, particularly diacetyl which gives curd its flavor. The lactic acid reacting with casein, the milk protein coagulates it resulting in a fibrous texture and thick consistency of curd.
Yogurt on the other hand is prepared by fermentation of milk with the help of bacterial strains that include: Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus. For yogurt preparation, a specific amount of yogurt culture is used for milk inoculation and it is incubated at a certain temperature over a specific time to form yogurt until the pH lowers around 4 to 4.4
Nutritional profile and probiotic content
- Yogurt is exceptionally rich in calcium and protein, minerals, and vitamins, with some differences based on the type of yogurt. Curd is also rich in calcium and protein however its nutritional content is highly influenced by the type of milk used in the process.
- The lactose in the milk is broken down more effectively by the bacterial cultures in yogurt than in curd hence yogurt is better digested by the people with lactose intolerance. Curd and Yogurt both contain probiotics, although yogurt has a higher probiotic content attributed to specific added strains during preparation.
- Yogurt has a higher probiotic content as compared to traditional curd. Curd is rich in vitamins B-12, A, and D with healthy fats and minerals including potassium, magnesium, and calcium.
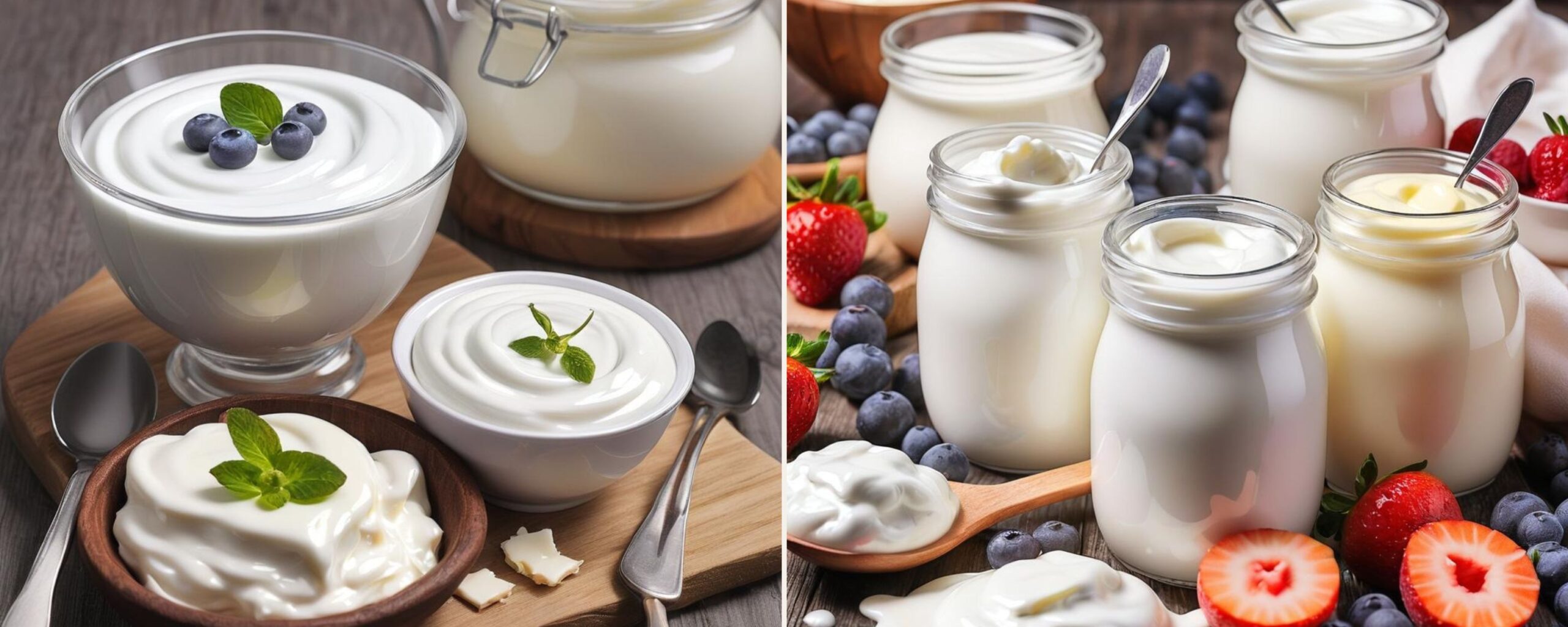

Uses of Yogurt and Curd
- Curd is typically used in savory recipes in South Asian and Indian cuisines to make dips such as raitas, curries, and recipes requiring creamy textures and tangy flavors. It is also used in baking.
- Whereas yogurt is mainly used in Western cuisines, particularly in sauces, dips, and smoothies. It can be easily substituted for mayonnaise and sour cream due to its properties. Its texture works best when used in desserts, toppings, and salad dressings.
Yogurt Vs Curd
Curd and Yogurt are both dairy products prepared in distinct ways and hence contain different nutritional compositions, textures, and tastes.
While both contain some amount of similarities their different properties showcase cultural preferences and methods of production. Both of the dairy delicacies hold significant culinary value. It can be dependent on personal needs of nutrition to determine which one is healthier. Factors such as flavor preferences, dietary needs, and intended use have to be considered to choose one from the two.
Author: Sanika Pande
- Medicine and Diseases
- Nutrition and Diet