Understanding Folliculitis: Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention Tips
Overview:
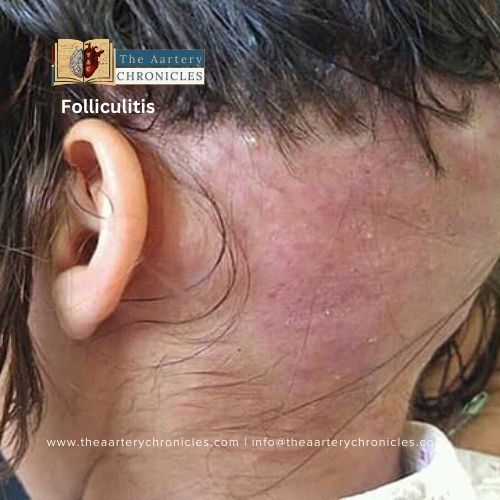
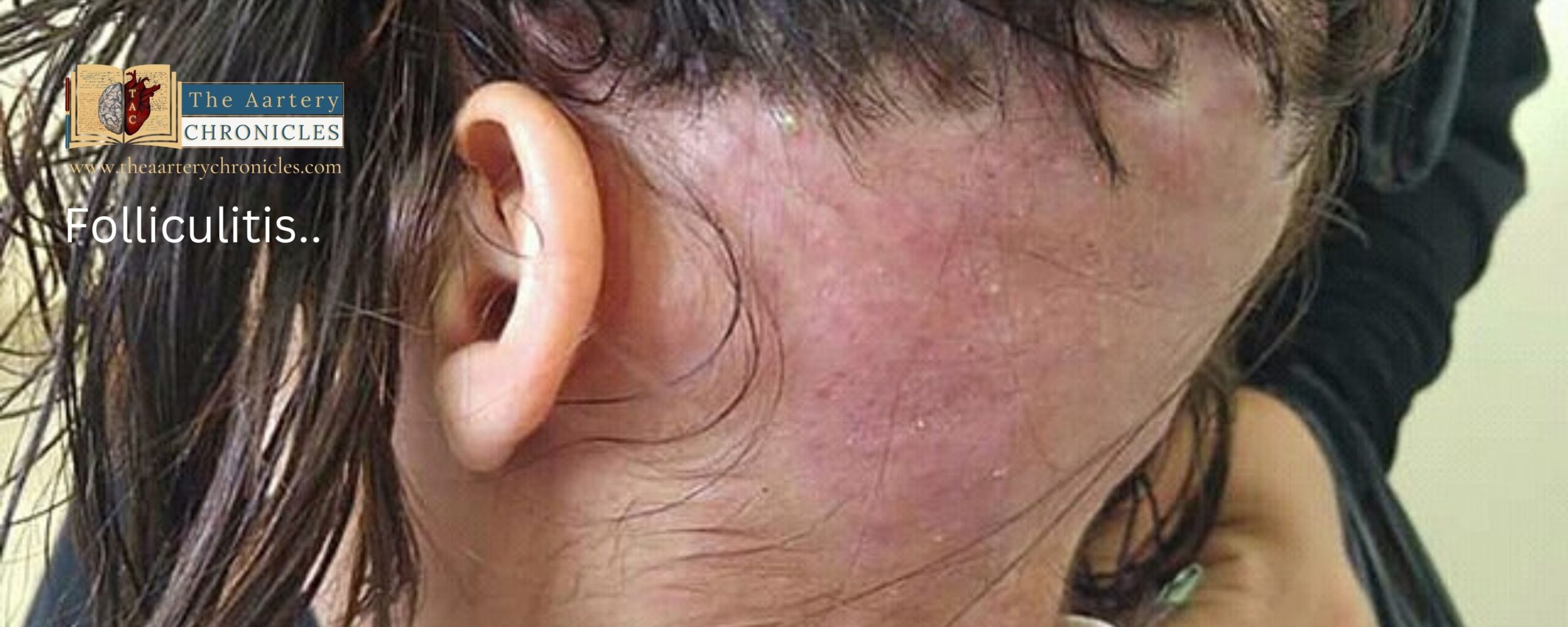
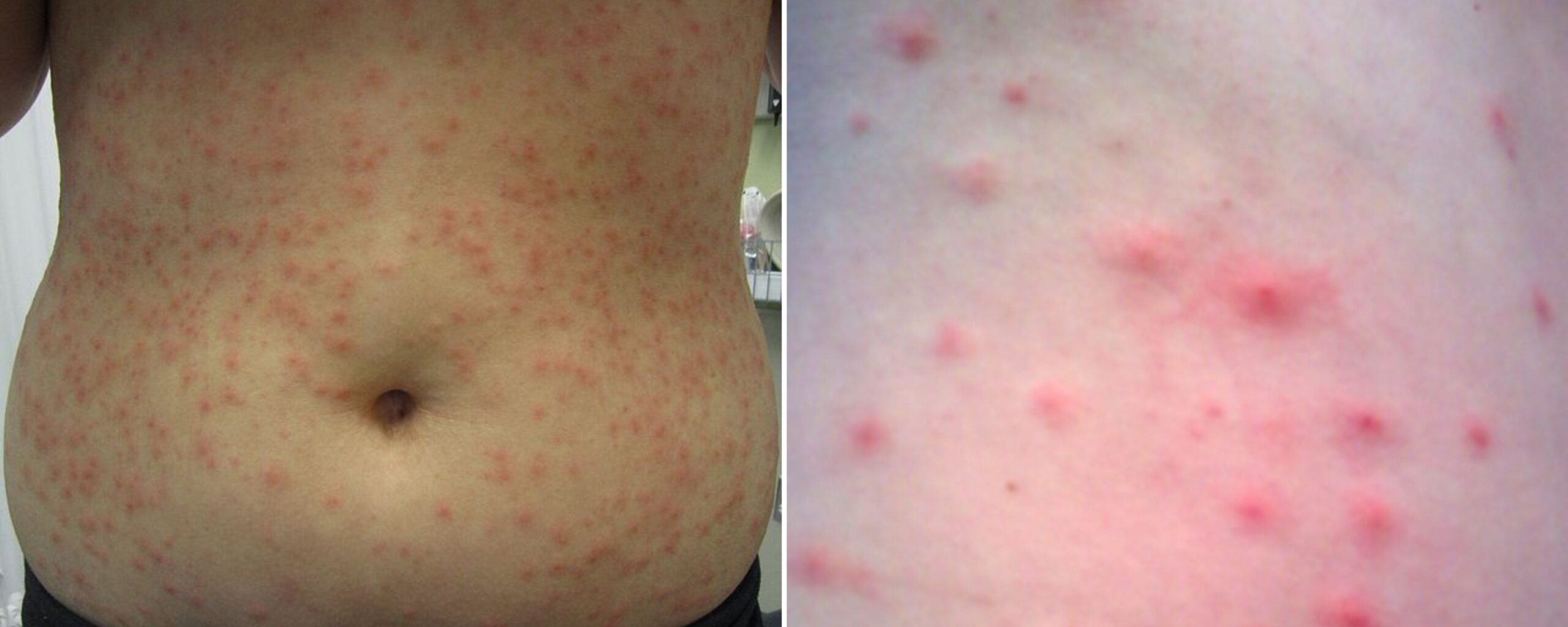
Folliculitis is a common condition that causes inflammation in hair follicles. It involves the presence of inflammatory cells in the walls of hair follicles and Ostia, resulting in a rash with red, itchy bumps that may cause mild pain. Folliculitis can potentially affect any part of the body except for the palms of the hands, soles of the feet, and lips. Mild cases of folliculitis may go away on their own with basic hygiene practices and self-care. However, severe and repeated infections require medical attention, as chronic infections may result in permanent hair loss. In some cases, the spread of infection can lead to the formation of crusty sores
Causes of folliculitis:
Most often an infection with bacteria, Staphylococcus aureus is a prime cause of folliculitis. Other contributing factors may include viruses, parasites, fungi, or bacteria that thrive in tubs, medications, or medical conditions.
Infections of hair follicles by staph in the beard area lead to barber’s scratch, which becomes chronic due to shaving. Another similar infection caused by a fungus is Tinea barbae. Pseudofolliculitis barbae, prevalent in African American men, results from overcutting of curly beard hairs, causing them to curl back into the skin and become inflamed.
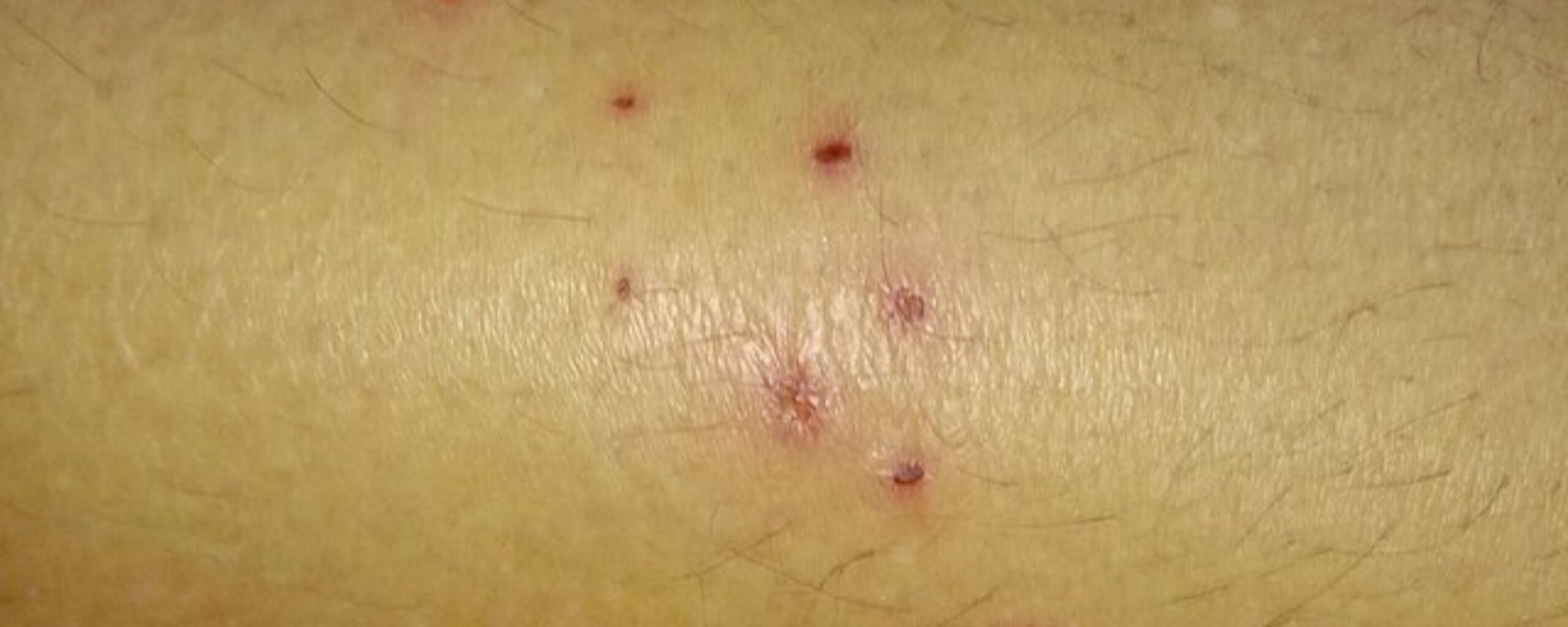
Risk factors for folliculitis:
Various factors that can contribute to the development of folliculitis may include
- Wearing tight clothing: Friction from tight clothes, like boots, rubber gloves, or sports equipment, can contribute to folliculitis.
- Sweating: Excessive trapped sweat, resulting from improper hygiene practices, may lead to infection.
- Ingrown hair: Shaved hair regrowing and curling into the skin can cause irritation and infection.
- Blockage of hair follicles: Heavy moisturizers, serums, medicines, sports gear, bandages, and casts can block hair follicles, leading to skin infections.
- Hot tub use: Frequent use of poorly maintained hot tubs, public pools, or whirlpools.
- Excessive waxing or shaving: Damages hair follicles, and wearing wigs, oils, and tight hairstyles can cause traction.
- Medications: Including chemotherapy drugs, prednisone, corticosteroid creams, and long antibiotic acne treatments.
- Hyperhidrosis and dermatitis: Conditions that contribute to excessive sweating and skin inflammation.
- Other medical conditions: Such as AIDS/HIV, which can lower immunity and resistance to infections
Signs and Symptoms of folliculitis
The symptoms of folliculitis are highly dependent on the severity of the condition. Some of the common symptoms are:
- Pimples near follicles
- Rashes
- Itchy and irritated skin
- Tenderness of the scalp
- Inflamed bumps on the skin
- Appearance of pus blisters near hair follicles, neck, genitals, or groin.
Diagnosis and Treatment Insights for folliculitis
Effective diagnosis of folliculitis involves assessing medical history, medications, and skin appearance. In rare cases, tests like skin swabs for culture, skin biopsy, or scrapings may be recommended for infection determination.
Treatment options vary based on the underlying cause and severity. Mild cases often respond to basic hygiene practices and over-the-counter antifungal or antibacterial creams, while more severe cases may necessitate prescription drugs, including oral or topical antibiotics, antifungal agents, or antiparasitic agents.
Diagnosis and treatment Insights for folliculitis
Effective diagnosis of folliculitis involves assessing medical history, medications, and skin appearance. In rare cases, tests like skin swabs for culture, skin biopsy, or scrapings may be recommended for infection determination.
Treatment options vary based on the underlying cause and severity. Mild cases often respond to basic hygiene practices and over-the-counter antifungal or antibacterial creams, while more severe cases may necessitate prescription drugs, including oral or topical antibiotics, antifungal agents, or antiparasitic agents.
Long-term complications of folliculitis
There are certain complications associated with prolonged or severe cases of folliculitis.
- Permanent scars
- Repeated infections
- Hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation
- Permanent loss of hair
- Permanent damage to hair follicles
Tips for Preventing Folliculitis
- Practice Good Hygiene:
- Cleanse skin regularly with a mild, non-comedogenic soap or cleanser.
- Ensure thorough washing after sweating or any activity that causes skin contact.
- Avoid Tight Clothing:
- Opt for loose-fitting clothing to reduce friction and irritation.
- Opt for breathable fabrics like cotton to reduce sweat retention
- Proper Hair Removal Techniques:
- Use clean, sharp razors when shaving.
- Shave in the direction of hair growth to prevent ingrown hairs.
- Consider alternative hair removal methods, such as waxing or depilatory creams.
- Moisturize Wisely:
- Choose non-comedogenic moisturizers to avoid clogging hair follicles.
- Apply moisturizers after hair removal to soothe the skin.
- Maintain Clean Tools:
- Regularly clean and disinfect razors, trimmers, and other hair removal tools.
- Limit Hot Tub Use: Ensure hot tubs, public pools, and whirlpools are properly maintained and cleaned.
- Manage Underlying Conditions: Control conditions like hyperhidrosis or dermatitis through proper medical management.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices:
- Maintain a balanced diet to support overall skin health.
- Stay hydrated to promote skin hydration.
- Seek Prompt Treatment:
- Address any signs of infection promptly to prevent complications.
By incorporating these tips into your routine, you can reduce the risk of developing folliculitis and promote healthier skin. If symptoms persist or worsen, consult a doctor for guidance.
Conclusion
Folliculitis is a condition that can be prevented easily with proper hygiene practices. It is necessary to seek medical help in case of repeated infections, or if the symptoms persist longer than 2 to 3 days. Precautions must be taken while indulging in any kind of hair removal treatment. Hair removal items such as razors, trimmers, or scissors must be regularly cleaned after use. Maintaining personal hygiene is essential as well especially if you have sensitive skin. Mindful use of products such as shampoos and body washes is essential, it is important to avoid products that may cause allergies. Hair oils should be washed off within 45 minutes to a few hours to avoid clogging of follicles. By integrating these practices, you actively safeguard against folliculitis and nurture healthier skin.
Author: Sanika Pande
Reviewed by: Dr Aarti Nehra,
MBBS, MMST
- Medicine and Diseases
- Nutrition and Diet