Understanding Erectile Dysfunction: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment Options and Approaches
Erectile dysfunction (ED) refers to the incapability to achieve or sustain an erection sufficient for sexual intercourse. Did you know that as per research, 1 in 10 men will experience erectile dysfunction at some point in their lifetime? In the year 1995, more than 152 million men worldwide were estimated to have experienced ED. It’s predicted that by 2025, the global prevalence of ED will reach around 322 million.
What is Erection?
Erection is a physiological response represented by the enlargement and engorgement of the penis. This complex process involves the harmonious functioning of various systems such as endocrine, neurological, circulatory, and musculoskeletal processes. The autonomic nervous system, comprising the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems, primarily regulates this response.
The sensory signals from the genital area are transmitted to the brain after a man experiences sexual stimulation or sexual arousal. In response, the brain sends signals back to the genital area through the parasympathetic nervous system. These signals stimulate the release of nitric oxide, which relaxes the smooth muscles of the blood vessels in the penis. When these blood vessels relax and dilate, they allow an increased flow of blood into the spongy corpora cavernosa of the penis. This heightened blood flow causes the corpora cavernosa to become engorged, resulting in an enlarged and erect penis. Simultaneously, the veins responsible for draining blood from the penis are compressed, aiding in the maintenance of the erection.
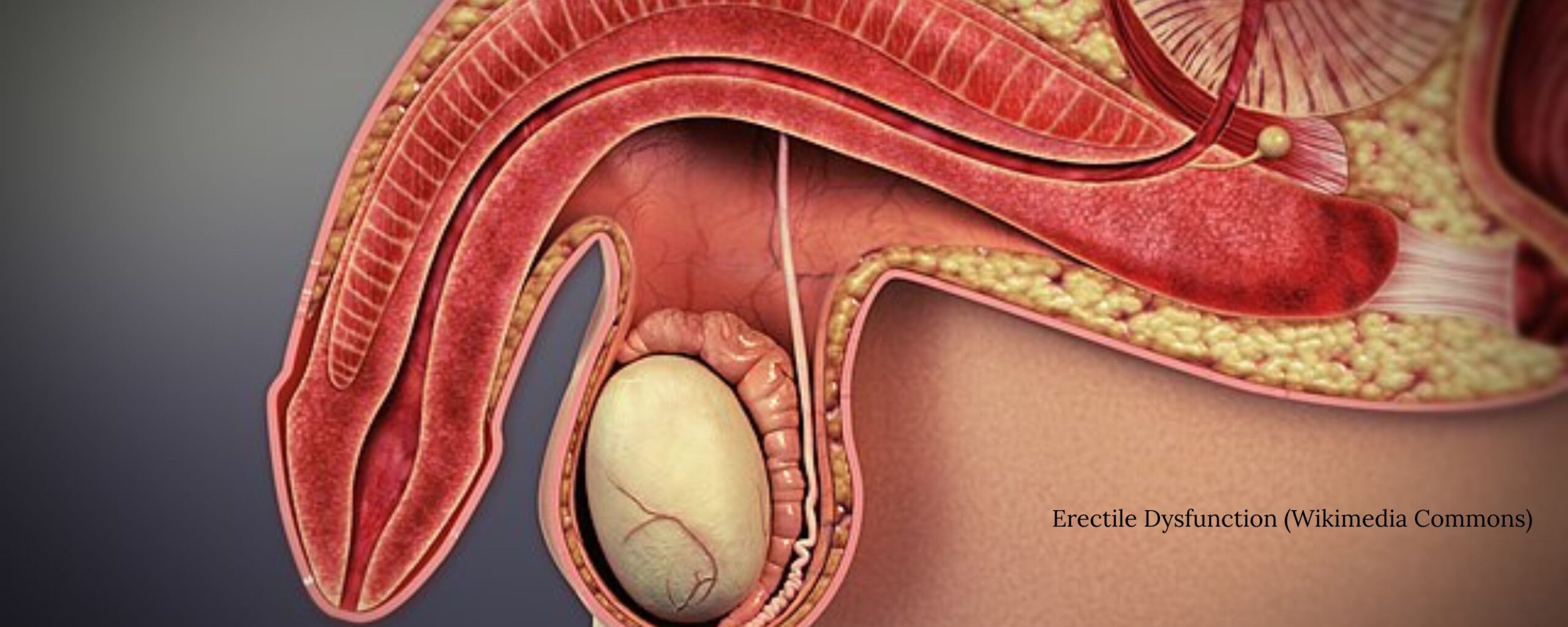
What is Erectile Dysfunction?
Erectile Dysfunction (ED) can be referred to as a persistent incapability to attain or maintain an erection required for satisfactory sexual intercourse. ED is believed to be a prevalent medical condition that can impact the quality of an individual’s life.
Did you know that research indicates ED is more widespread among older males, but it also affects a significant number of younger males?
What are the Symptoms of Erectile Dysfunction?
Symptoms of erectile dysfunction comprise:
- Difficulty in getting an erection
- Complete inability to get an erection
- Inability to maintain an erection
- Only occasionally being able to get an erection.
- Low self-esteem
- Distress and depression
Additional sexual disorders linked to ED may encompass Premature ejaculation, Delayed ejaculation and Anorgasmia, which is the inability to attain orgasm even after sufficient stimulation
What causes erectile dysfunction?
Erectile dysfunction (ED) can result from various factors, and it often involves a combination of physiological, psychological, and relational components. The common ED causes include the following:
- Diabetes
- Age over 50
- Radiation therapy or other injuries from treatments for prostate cancer or surgery
- Cardiovascular diseases
- Smoking
- Kidney diseases
- Obesity
- A sedentary lifestyle and lack of movement
- High cholesterol
- Drug and alcohol abuse
- Emotional issues such as depression, conflicts in relationships, stress
Organic etiologies such as neurogenic, drug interactions, Peyronie’s disease (PD), and endourologic causes may be responsible. Men with diseases such as multiple sclerosis, trauma, or epilepsy are believed to be at greater risk of developing erectile dysfunction. Medications such as NSAIDs, antiepileptics, antidepressants, and neuroleptics can also cause erectile dysfunction. Possible etiologies of hormonal abnormalities such as acquired hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, congenital hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, and Klinefelter’s syndrome may result in ED. Alterations in the components of erectile response, whether relational, psychological, or organic, can be factors in erectile dysfunction.
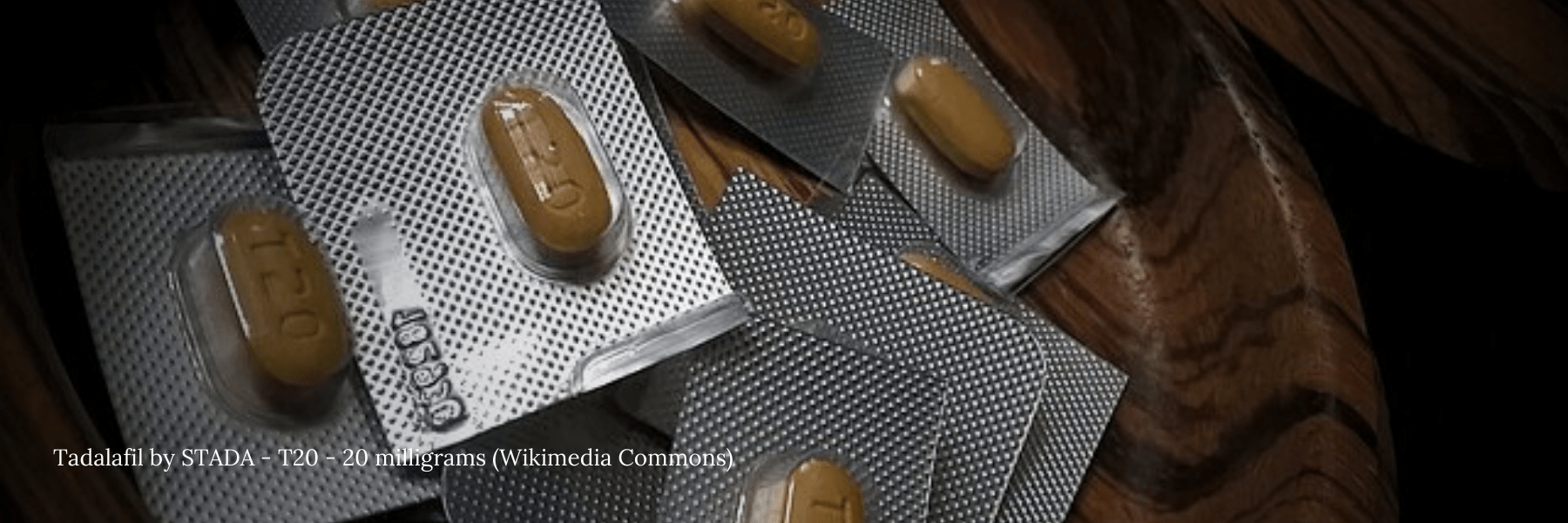

Available Treatment Options for Erectile Dysfunction:
Oral Drugs:
Mostly PDE type-5 inhibitors are used as they help increase penile blood flow. Oral drugs are advised to be taken 45- 60 minutes before sexual activity. The drugs provide normal functioning and erectile responses. However, PDE5 inhibitors should be avoided in the case of individuals with heart disease.
Common drugs include:
- Tadalafil (Cialis)
- sildenafil citrate (Viagra)
- Avanafil (Stendra)
- vardenafil HCl (Levitra)
Testosterone therapy:
The combination of PDE5 inhibitors and testosterone therapy may help fix the rare cases of low sex drive and low testosterone levels resulting in relief from ED symptoms.
Self-injection therapy: A dose of alprostadil is administered to the side of the penis, with the dosage adjusted based on the condition’s severity. On occasion, a combination of two other drugs alongside ICI (Intracavernosal Injection) alprostadil may be used.
Intraurethral Therapy: A medicated drug pellet of Alprostadil is inserted in the urethra.
Surgical treatment: A penile implant is inserted as the primary surgical treatment for ED. Patients who have failed oral pills, self-injections, or other therapies opt for surgical treatments.
It’s important to note that the choice of treatment depends on the specific underlying causes of ED, the individual’s overall health, and their preferences.

MED3000 (Eroxon)
In June 2023, the FDA approved the first-ever over-the-counter gel for erectile dysfunction, known as MED3000. This gel is applied directly to the penis just before intercourse and is available in single-use tubes. It contains various volatile compounds that stimulate penile nerve endings, leading to increased blood flow, a crucial factor for achieving an erection. Some reports suggest that the gel can lead to an erection within just 10 minutes, while commonly prescribed ED drugs like Viagra typically take around 30-40 minutes to take effect. MED3000 is now approved in multiple countries, including those in Africa, the Middle East, and Europe. It is available in the UK and can be purchased online. Eroxon introduced it for online sales in the Benelux region and made it available in retail pharmacies throughout Belgium in March 2023, with plans for additional online and retail releases in the coming months.
Conclusion:
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a prevalent condition affecting approximately 30 million men. It can be attributed to underlying health issues or the natural aging process. Fortunately, numerous treatment options, therapies, and medications are available. However, it’s crucial to assess the severity of the condition and consult with a healthcare professional before selecting a treatment. Adopting a healthy lifestyle is also vital for managing ED effectively, which includes maintaining a balanced diet, regular exercise, smoking cessation, and limiting alcohol consumption. Making these positive changes can help alleviate ED symptoms in the long term.
- Ludwig W, Phillips M. Organic causes of erectile dysfunction in men under 40. Urologia internationalis. 2014 Jan 1;92(1):1-6.
- Heaton JP, Adams MA. Causes of erectile dysfunction. Endocrine. 2004 Mar;23:119-23.
- Rew KT, Heidelbaugh JJ. Erectile dysfunction. American family physician. 2016 Nov 15;94(10):820-7.
- Wessells H, Joyce GF, Wise M, Wilt TJ. Erectile dysfunction. The Journal of Urology. 2007 May 1;177(5):1675-81.
- Kim S, Cho MC, Cho SY, Chung H, Rajasekaran MR. Novel emerging therapies for erectile dysfunction. The World Journal of Men's Health. 2021 Jan;39(1):48.
- Andersson KE. Pharmacology of penile erection. Pharmacological reviews. 2001 Sep 1;53(3):417-50.
- Andersson KE. Mechanisms of penile erection and basis for pharmacological treatment of erectile dysfunction. Pharmacological reviews. 2011 Dec 1;63(4):811-59.
- Schultheiss D, Stief CG, Truss MC, Jonas U. Pharmacological therapy in erectile dysfunction--current standards and new viewpoint. Wiener Medizinische Wochenschrift (1946). 1997 Jan 1;147(4-5):102-4.
Author: Ms Sanika Pande
Reviewed by Dr. Aarti Nehra