Toothache Troubles? Know All the Possible Causes and Remedies
Introduction
National Toothache Day, observed on February 9, 2024, may seem like an unusual commemoration; however, this day is marked to raise awareness about tooth pain and to advocate effective solutions for a healthy, pain-free smile. This day highlights the importance of dental care and preventive measures while acting as a global reminder of dental health.
Toothache is a common dental problem that can range from mild discomfort to excruciating pain, affecting our ability to eat, sleep, and carry out daily activities. A toothache can be brought on by a variety of factors, including oral infections, food particles lodged between teeth, and dental decay. Sometimes, it can also be caused by transient inflammation or irritation in the gums and surrounding oral tissues.
Understanding the causes, seeking timely relief, and adopting preventive measures are crucial steps in managing toothaches effectively.
What is a toothache?
Toothache refers to pain or discomfort in and around the mouth or teeth. The pain ranges from mild and intermittent to severe and chronic. It is typically a symptom of an underlying dental issue, such as dental decay, gum disease, or tooth sensitivity. [1]
Although toothaches are typically not life-threatening, they might occasionally be an indication of a serious disease that calls for immediate medical attention.

Causes of Toothache
It is crucial to understand the different causes of toothache to avoid aggravation of the condition and seek appropriate treatment.
Some of the possible causes of toothache are as follows:
It is crucial to understand the different causes of toothache in order to avoid aggravation of the condition and seek appropriate treatment.
Some of the possible causes of toothache are as follows:
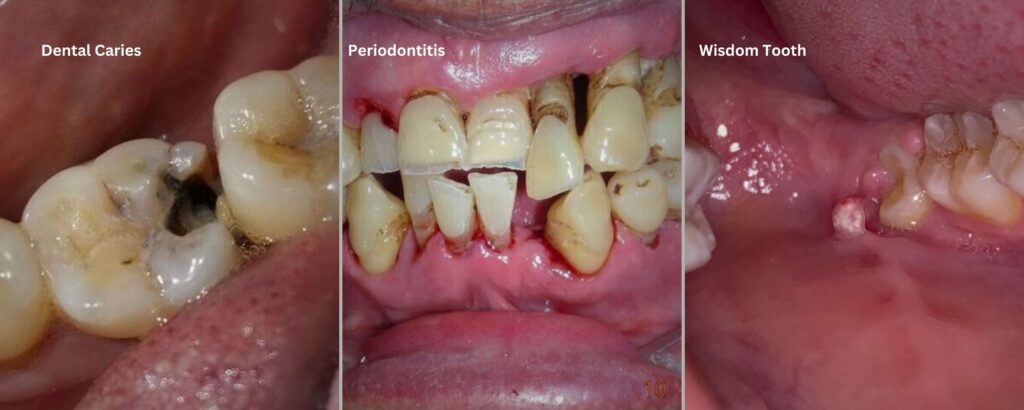
- Dental decay: Dental caries (cavity) is the most prevalent cause of toothache, as it exposes the sensitive inner layers, causing dental pain.
- Gum disease: Infections or inflammation of the gums can cause pain, especially when left untreated.
- Impacted third molar (wisdom tooth): When a wisdom tooth is impacted, it may exert pressure on the surrounding teeth as it tries to push through the gum tissue. This pressure can cause discomfort or pain in adjacent teeth, leading to a toothache.
- Tooth abscess: A tooth abscess is a pocket of pus that forms around the root of a tooth due to a bacterial infection that reaches the dental pulp. An abscessed tooth results in constant, throbbing pain.
- Tooth trauma: Accidents or injuries to the teeth can result in fractures or nerve damage, triggering pain.
- Bruxism: Bruxism is characterised by teeth grinding or clenching, and the enamel wears thin due to the pressure applied by the gnashing of teeth, resulting in pain or sensitivity.
- Tooth sensitivity: Exposed tooth roots due to gum recession or enamel erosion can lead to tooth sensitivity to hot, cold, or sweet food items. [2, 3]
Some other causes of toothache include:
- Sinusitis
- Worn or dislodged dental filling
- Trigeminal neuralgia [4]
What are the Symptoms of Toothache?
Tooth pain may be dull, sharp, throbbing, or achy in nature and can radiate to other parts of the face, jaw, or head. Depending on the underlying reason, a toothache can present itself in a variety of ways. Some of the common symptoms of toothache are as follows:
- Dull and persistent pain
- Sharp and throbbing pain
- Painful tooth sensitivity to hot, cold, or sweet food items and drinks
- Pain is aggravated while chewing or biting
- A headache
- Foul smell from teeth
Fever - Headache or earache
- Redness and swelling in and around the gums
- Burning, non-pulsatile pain [1, 2, 5, 6]
Management and Treatment Of Toothache
Managing toothache entails relieving pain while addressing the root cause. Some effective strategies for pain relief are as follows:
- Dental Restoration: In this procedure, the decayed portion of the teeth is removed and replaced with durable dental filling material.
- Root Canal Treatment: For severe tooth decay or infection that has reached the dental pulp (the innermost part of the tooth containing nerves and blood vessels), root canal therapy may be needed to remove the infected tissue and seal the tooth with a filling material.
- Tooth Extraction: In cases where a tooth is severely damaged or cannot be saved, the dentist may recommend extracting the tooth to alleviate pain and prevent further complications.
- Periodontal Therapy: If gum disease is contributing to the toothache, the dentist may employ periodontal therapy that involves deep cleaning procedures such as scaling and root planning to remove plaque and tartar buildup from the teeth and gums. [1,2]
Home Remedies for Toothache
While home remedies can temporarily relieve toothache while awaiting professional dental treatment, they should not be used in place of professional dental care. Here are some effective home remedies to alleviate toothache discomfort:
- Saltwater rinse: Due to its inherent disinfecting properties, saltwater relieves pain and discomfort by lowering inflammation in the area surrounding teeth and gums. This involves rinsing the mouth with 1/2 teaspoon salt and a glass of warm water. [2]
- Cold compress: Apply a cold compress or ice pack wrapped in a cloth to the outside of the cheek near the affected tooth. Cold therapy can help numb the area and reduce swelling, providing temporary relief from toothache discomfort. [2]
- Hydrogen peroxide: Hydrogen peroxide, an oxidising chemical known for its antiseptic properties, is an effective home remedy to relieve tooth pain. It can be used as a mouthwash by diluting 3% hydrogen peroxide with equal parts water. [7]
- Vanilla extract: Vanilla extract contains alcohol, which can help numb the affected tooth and reduce pain. The extract can be applied either by dabbing the affected area with a cotton ball or with the fingertips. [8]
- Garlic: Garlic has been used for its antibacterial and analgesic properties throughout history. A fresh garlic clove can be crushed to release its juices and applied directly to the painful tooth for a few minutes to relieve toothache and prevent infection. [9]
- Clove oil: Clove oil is a natural remedy that has been used to treat toothaches for ages. Clove oil contains eugenol, a potent natural anaesthetic that can help numb the affected tooth and reduce pain. It is used by diluting clove oil with a carrier oil, such as sunflower or jojoba. The National Association of Holistic Aromatherapy recommends using a ratio of around 15 drops of clove oil to one ounce of carrier oil. Clove oil can be used as a topical anesthetic by dabbing the diluted oil on the affected region with a cotton ball or as a mouthwash by mixing a drop of oil with a glass of water.
- Over-the-counter (OTC) pain medications: While painkillers and antibiotics can reduce dental pain and tenderness, their benefits are only momentary. Over-the- counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can be used to provide temporary relief . [2]
How to Prevent a Toothache?
Preventing toothache involves maintaining good oral hygiene habits and addressing dental issues promptly. Some preventive measures to reduce the likelihood of developing toothache are as follows:
- Brushing and flossing: Brushing teeth at least twice a day and flossing daily to remove plaque and food debris, prevents tooth decay and gum disease.
- Regular dental check-ups: Regular dental visits for professional cleaning and dental check-ups can help detect and address dental issues early on.
- Balanced diet: Limiting sugary and acidic food items and beverages, which contribute to tooth decay and erosion.
Toothache: When to seek emergency care?
One should seek immediate medical care if:
- The toothache lasts more than a day or two
- Toothache is excruciating in nature and is accompanied by fever and chills
- Develop swelling in the cheek or jaw and difficulty in breathing
- A tooth abscess (when bacterial infection in the tooth forms a pocket of pus) that requires draining and/or causes fever and swelling on the side of the face or neck
- Experience earache or pain while mouth opening [10, 11]
Conclusion:
Toothache is one of the most common causes of oral pain, and it may be caused by a variety of factors such as dental decay, gum disease, tooth abscess, or trauma. Toothache can range from dull and persistent to a sharp, throbbing ache, which might be sometimes accompanied by swelling, fever, chills, or a headache. While home remedies like warm saline rinse, cold compress, and hydrogen peroxide rinse might provide temporary relief from pain, it is important to visit a dentist for a permanent solution. Treatment for toothache varies depending on the underlying cause and the severity of the pain. Dental fillings, root canal treatment (RCT), extraction, and periodontal therapy are some of the available treatment options.
- Managing tooth pain in general practice - PMC (nih.gov)
- Toothache: Symptoms, Causes & Remedies (clevelandclinic.org)
- Toothache: First aid - Mayo Clinic
- 7 Causes for Your Toothache (clevelandclinic.org)
- Understanding and managing dental and orofacial pain in general practice | British Journal of General Practice (bjgp.org)
- Nonodontogenic toothache - PubMed (nih.gov)
- Hydrogen Peroxide on Toothache: 4 Effective Relief Methods (worldofdentistry.org)
- Studies on the antioxidant activities of natural vanilla extract and its constituent compounds through in vitro models - PubMed (nih.gov)
- Garlic: a review of potential therapeutic effects - PMC (nih.gov)
- Toothaches: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia
- Tooth abscess: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia

Author: Dr. Anjali Singh
BDS [KGMC, Lucknow]
- Medicine and Diseases
- Nutrition and Diet
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.