Safeguarding Oral Health During Pregnancy
An Overview
Pregnancy is a normal physiological process that brings about transitory changes in women’s physical structure, hormone levels, metabolism, and immune systems. Although the physiological, hormonal, and dietary changes brought on by pregnancy are essential for maintaining the stable state of both the mother and the foetus, they also tend to increase the risk of oral diseases such as periodontitis and dental caries. These pregnancy-induced changes alter the microbial composition of different body sites in pregnant women, including the oral cavity. Changes brought to the oral microbiome during pregnancy might impact maternal and neonatal oral health and birth outcomes.
Therefore, it is crucial to comprehend oral flora changes during pregnancy and their implications on maternal and birth outcomes. So, let’s dive into this article to gain a deeper understanding of the dental health risks associated with pregnancy and tips to maintain good oral health and hygiene during pregnancy. [1]
How does pregnancy impact oral health?
Pregnancy-induced physiological, hormonal, and dietary changes can affect the teeth and gums in the following ways:
- Hormonal fluctuations: Fluctuating levels of oestrogen and progesterone during pregnancy increase the likelihood of dental infections by making the mouth more absorbent and the host’s immune system less effective.
- Dietary changes: During the first few months of pregnancy, some women experience cravings for certain types of food, especially carbohydrates. Some pregnant women tend to develop an eating disorder called pica, which causes them to consume non-edible things like chalk, ice, and clay. These dietary changes brought on by pregnancy might harm the dental health of pregnant women.
- Morning sickness: Morning sickness in the form of nausea and vomiting is a common occurrence during the first few months of pregnancy. Vomiting increases the acidic environment of the oral cavity, which may lead to dental conditions like tooth erosion.
- Neglect of oral hygiene: Pregnant women tend to neglect their oral health and hygiene, which may harm teeth and gums and further deteriorate maternal oral health. [1, 2, 3]
Common Dental Conditions During Pregnancy
Pregnant women have an increased risk of having certain dental conditions. Hormonal, behavioural, and physical changes can all have an impact on your dental health.
The most prevalent dental conditions that arise during pregnancy include the following:
- Gingivitis (bleeding gums): Gingivitis is characterized by red, swollen, bleeding gums. Fluctuations in oestrogen and progesterone levels during pregnancy weaken the body’s defences against bacterial plaque and increase blood flow to gum tissue, which results in gingival (gum) inflammation. [4]According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), 60-75% of pregnant women develop pregnancy gingivitis. [5]
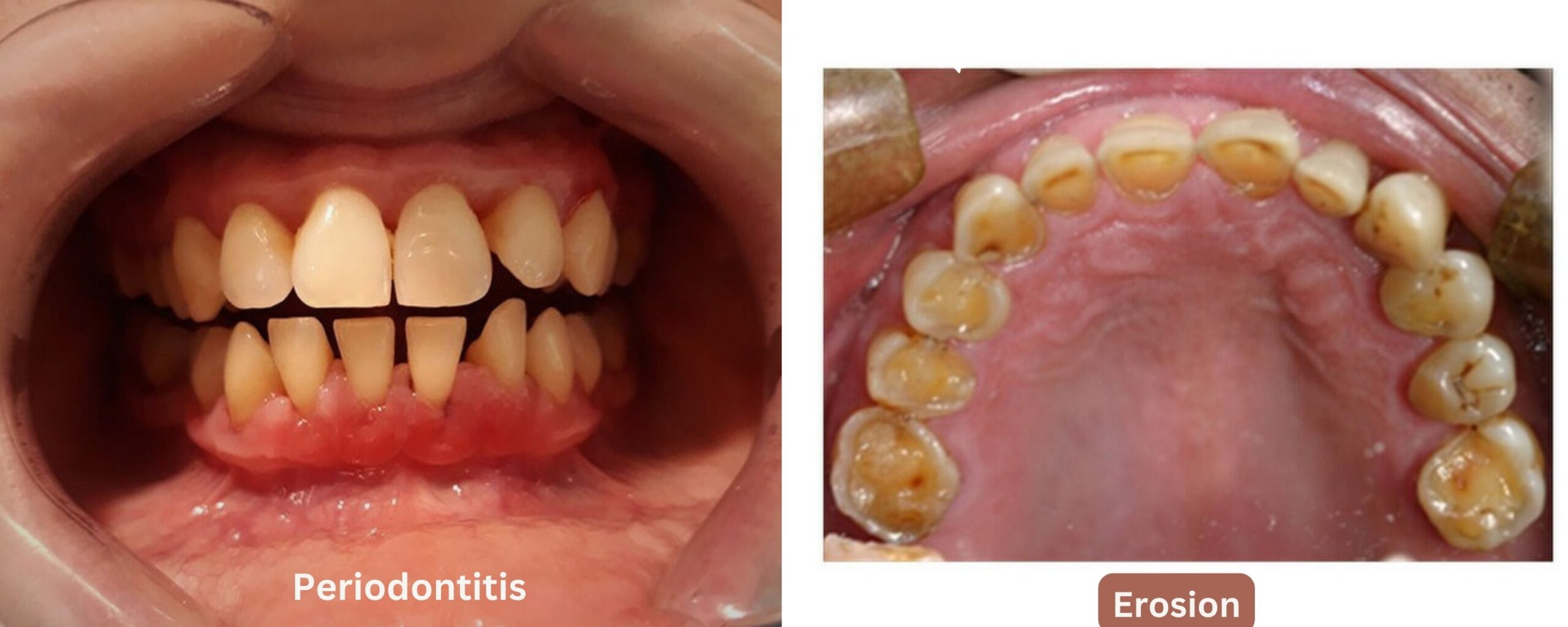
- Periodontitis (gum disease): If gingivitis is left untreated it can lead to periodontal disease. It causes gum infection and loss of periodontal bone that supports the teeth, causing the teeth to become loose and eventually fall out. Periodontitis is characterized by tender gums, gum recession, periodontal pockets, loss of periodontal bone, and tooth mobility. Periodontitis may lead to poor pregnancy outcomes, including preterm birth and low birth weight. [5]
- Dental Caries (tooth decay): Pregnant women tend to be at an increased risk of dental cavities due to frequent snacking and dietary changes. Untreated cavities might lead to the transmission of cavity-causing bacteria to the baby during pregnancy and after delivery. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), one in four women of childbearing age have untreated cavities, and children are three times more likely to develop caries if their mothers have elevated levels of untreated dental caries or tooth loss.
- Dental erosion: Vomiting and acid reflux are common occurrences during pregnancy, which causes stomach acid to rise into the mouth. These stomach acids are potent in nature and have the potential to harm the teeth by causing dental erosion. Frequent exposure of teeth to stomach acid might cause the outer surface of teeth (enamel) to wear away, and this is known as dental erosion. [6]
- Pregnancy tumours: Pregnancy tumours also known as granuloma gravidum, are a type of pyogenic granuloma that is non-neoplastic, reactive gingival overgrowth which appears due to hormonal changes that occur during pregnancy. These tumours are non-cancerous and seen as lumps red, raw lumps on the gums, usually between the teeth. These tumours regress spontaneously after pregnancy and, in rare cases, need to be surgically removed.
Dental Exams and X-rays During Pregnancy
Dental exams
Patients can see a dentist at any point throughout their pregnancy, but the second trimester is often considered the ideal time due to morning sickness, nausea, and mouth sensitivity that might make it difficult to see a dentist during the first trimester. Additionally, a pregnant woman may find it uncomfortable to lie on a dental chair due to her growing belly throughout the third trimester. [6] Preventive, diagnostic, and restorative dental treatments are safe to carry out throughout the pregnancy. [10] Additionally, it is safe to use X-rays, painkillers, and local anaesthetic during pregnancy when necessary to accurately diagnose and treat dental issues. [9]
Dental X-rays
It is important to let your dentist know that you are pregnant, especially if there’s a possibility you will require an x-ray. The dentist will wait until the baby is born. X-rays are part of routine dental treatment and are often required to assess the problems with teeth, gums, and bone around the mouth. Though X-rays taken during pregnancy do not pose any concerns to the unborn child, such as miscarriage or birth defects, repeated radiation exposure might potentially damage the body’s cells over time and raise the chance of developing cancer. Usually, dentists advise covering the chest and stomach with a lead apron during an x-ray in pregnant women to protect the mother and baby. [6, 8]
Tips to Maintain Oral health during pregnancy
It is important to practice good oral hygiene to maintain proper oral health and reduce the risk of developing dental health conditions during pregnancy. Some tips to maintain oral health and hygiene are as follows:
- Brushing and flossing: Brushing teeth twice a day using fluoride-containing toothpaste and flossing once a day can help keep the teeth and gums in a healthy state. Avoid brushing your teeth immediately after vomiting to prevent enamel damage.
- Reduce oral acid exposure: Reduce oral acid exposure through lifestyle changes, anti-emetics, or antacids. But don’t take any medications, even OTC medicines, without consulting with your healthcare provider first.
- Regular dental check-ups: Schedule regular dental check-ups with the dentist every six months, even during pregnancy, and let the dentist know if you are pregnant or trying to become pregnant.
- Eating healthy and limiting sweets: It is crucial to resist giving in pregnancy cravings and limit the intake of sugary, sticky, sweet treats. Instead, one should include fresh fruits, green vegetables, and nutritious food in their diet, which are less likely to cause tooth decay. Eating a balanced diet helps provide essential nutrients to the mother as well as the growing baby.
- Contact the doctor in case of craving inedible things: Pregnant woman should immediately contact their doctor in case of craving inedible things like chalk, clay, or ice. [9]
- Oral microflora and pregnancy: a systematic review and meta-analysis - PMC (nih.gov)
- Oral care in pregnancy - PMC (nih.gov)
- Oral Healthcare during Pregnancy: Its Importance and Challenges in Lower-Middle-Income Countries (LMICs) - PMC (nih.gov)
- Pregnancy Gingivitis: Causes, Treatment & Prevention (clevelandclinic.org)
- Pregnancy and Oral Health Feature | CDC
- Oral Health and Pregnancy - Australian Dental Association (teeth.org.au)
- Effective Management of a pregnancy tumour using a soft tissue diode laser: a case Report - PMC (nih.gov)
- Oral health and pregnancy: six things every mum needs to know | Oral Health Foundation (dentalhealth.org)
- Pregnancy and Oral Health | Johns Hopkins Medicine
- Pregnancy | American Dental Association (ada.org)

Author: Dr. Anjali Singh
BDS [KGMC, Lucknow]