FDA Approves EOHILIA: First Oral Medication for Eosinophilic Esophagitis
EOHILIA: FDA-approved for Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE). Learn about the efficacy and treatment for this disorder.
The FDA has recently granted approval for EOHILIA (budesonide oral suspension), marking a breakthrough as the first oral medication designed for eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) in patients aged 11 and above. Scheduled for release by the end of February, EOHILIA will be available in convenient single-dose stick packets, each containing 2 mg/10 mL of the suspension.
EOHILIA (budesonide oral suspension)- The Drug
EOHILIA (budesonide oral suspension) is a corticosteroid prescribed for a 12-week course in patients aged 11 years and older with EoE. The yellowish-white viscous suspension contains 2 mg of budesonide per 10 mL, exhibiting thixotropic qualities, allowing it to freely flow when shaken and becoming viscous upon swallowing.
The Clinical Trials
Approval for EOHILIA is grounded in the efficacy and safety demonstrated through two randomized, multicentre, placebo-controlled 12-week trials involving patients aged 11 to 56 and 11 to 42 with EoE. The trials showcased EOHILIA’s effectiveness in improving patient-reported outcomes and achieving histologic remission based on combined DSQ (Dysphagia Symptom Questionnaire) scores after 12 weeks.
Study-1 identified a few common adverse effects (≥2% of patients receiving EOHILIA at a higher rate than placebo), including headache, erosive esophagitis, throat irritation, gastrointestinal mucosal candidiasis, respiratory tract infection, and adrenal suppression.
What Is Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE)?
Eosinophilic esophagitis or EoE is an allergic disorder of the esophagus. It refers to inflammation in the esophagus, induced by a particular type of white blood cell known as eosinophil.
Prevalence and Incidence of Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE)
Prevalence and incidence rates of EoE have notably increased over the past two decades, with 19.1 cases per 100,000 people and 5.1 cases per 100,000 people per year, respectively. Most cases are diagnosed in the pediatric age or the third decade of life.
Diagnosis of Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE)
The diagnosis of eosinophilic esophagitis involves conducting an upper endoscopy and biopsy.
- Endoscopy findings: Development of rings, white plaques or patches and furrows in the esophagus.
Nevertheless, EoE can exist even when the esophagus appears normal, which is why biopsy samples are taken.
Esophageal Samples: These samples are analyzed to detect an excessive presence of eosinophils in the esophageal tissue.
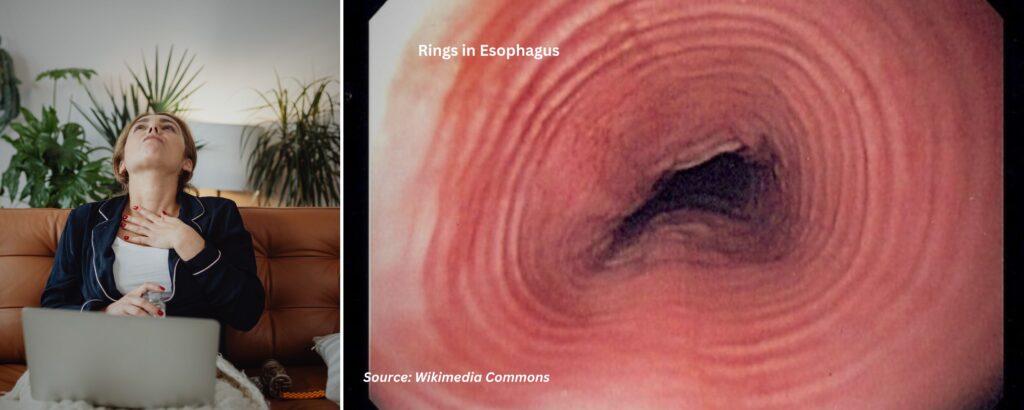
What are the Symptoms of Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE)?
Depending on the age symptoms may differ, however, a few common symptoms may include:
- Vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Spitting up
- Difficulty swallowing
- Abdominal pain
- Heartburn
- Irritability
- Issues with growth
- Reflux
- Poor weight gain in children
What are the Causes of Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE)?
Eosinophilic esophagitis is believed to be an immune-induced condition with response to an allergen that can be a certain food or environmental particles, however, the exact cause is not yet known. EoE is often linked with other allergic disorders such as food allergies, asthma, and atopic dermatitis. Genetic components may also cause an impact as it is known to run in families. A few environmental components include pollens, dust particles, molds, and mites.
Triggers of eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE)
Common food items that can trigger eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) are:
- Eggs
- A variety of seafood including shellfish
- Nuts (Typically peanuts and tree nuts)
- Dairy
- Derivatives of cow milk
- Wheat and gluten-containing products
- Soy
It is important to note that not everyone with EoE reacts to all of these food items, and the particular triggers may differ from person to person. The common risk factors for EoE include gender, as EoE affects three times as many men as women, pre-existing allergies and asthma, family history, the pollen season such as spring and fall, etc.
What is the Treatment of Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE)?
A few common treatment options include proton pump inhibitors, corticosteroids and some dietary changes. These approaches are often considered in managing EOE symptoms and addressing the underlying inflammation.
Source: Inputs from various media Sources
Sanika Pande
- Medicine and Diseases
- Nutrition and Diet
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.