Strawberry Hives: All that you need to know
Summary
Strawberry hives are allergic skin reactions to the consumption of strawberries. They range from as light as itchy red bumps to as serious as swelling or anaphylaxis. In this article, we explain what causes strawberry hives, how to recognise them, and the most effective treatments, ranging from over-the-counter drugs to home remedies. You will also know how to prevent them and remain safe if you are strawberry-sensitive.
Strawberry Hives: Causes, Symptoms & Quick Relief Tips
Hives are a skin reaction characterized by the appearance of itchy bumps or rashes on the skin. Strawberries are a food that can trigger hives in some people, particularly those who are allergic to them or sensitive to certain compounds in strawberries. Hives caused by strawberries typically appear shortly after consuming the fruit and can range from mild symptoms to more severe reactions. In this article, we’ll examine the causes of strawberry-related hives, common symptoms, and available treatments for this condition.
What Causes Strawberry Hives?
Strawberries contain several substances that can trigger allergic or hypersensitivity reactions, including:
1. Allergenic proteins: Some people are allergic to specific proteins in strawberries, which can trigger an abnormal immune response.
- This response leads to the production of histamine, a chemical that causes inflammation and the appearance of hives on the skin.
2. Natural Histamine in Strawberries: Strawberries naturally contain small amounts of histamine. In some people, this can increase histamine levels in the body and trigger an allergic reaction or skin rash.
3. Sensitivity to chemical additives: Sometimes hives aren’t caused by the strawberries themselves, but by chemicals or preservatives used during cultivation or storage. However, this cause is less common.
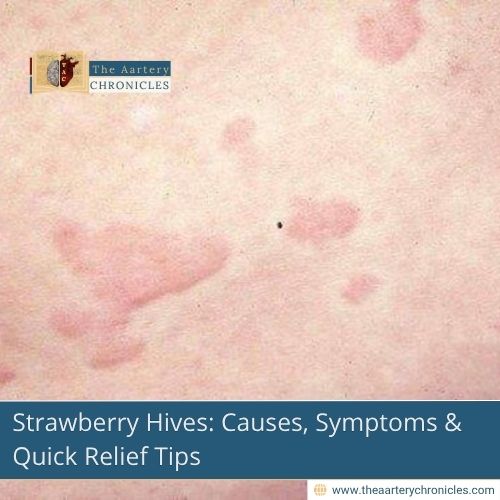
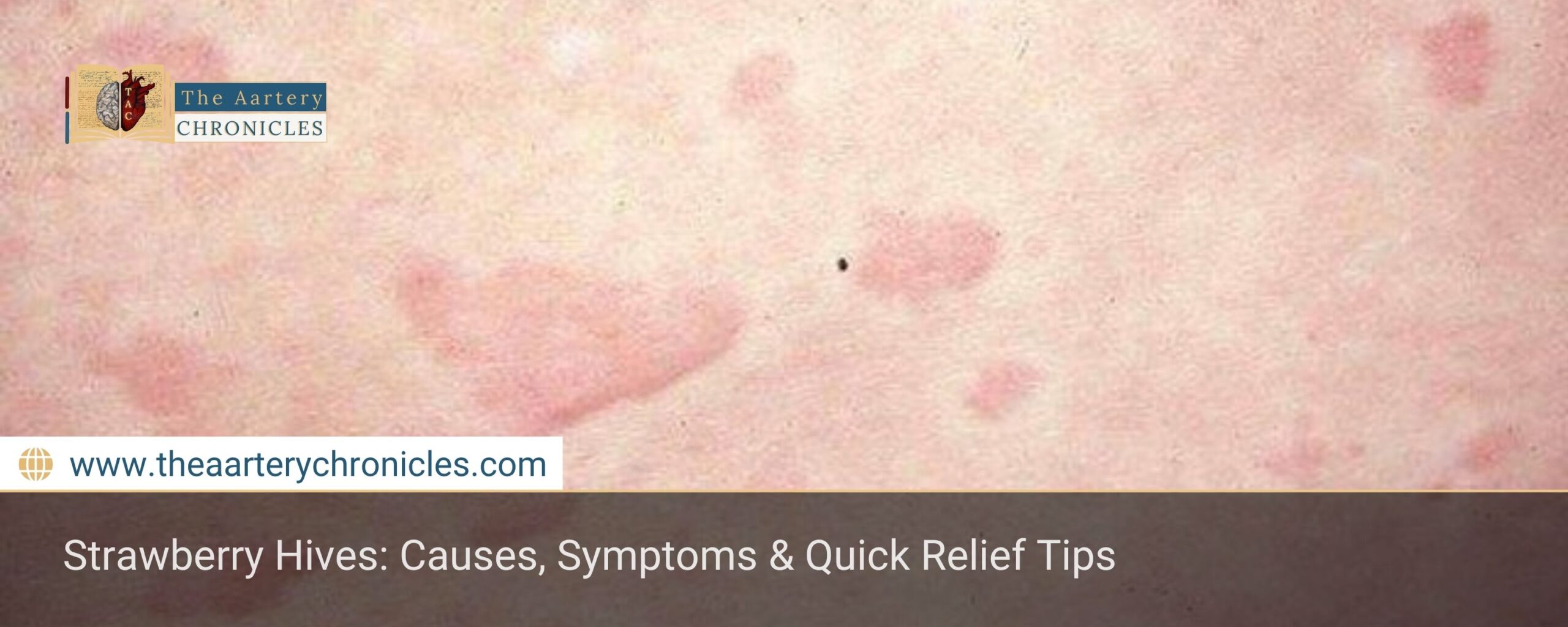
Strawberry Hives Symptoms
Strawberry-induced hives can appear quickly, usually within minutes or hours of eating the fruit. Typical symptoms include:
- Red, swollen bumps: Small, raised, itchy areas that may be red or white. They can appear anywhere on the body.
- Itching: Severe itching is the most common symptom and may be localised only around the hives or spread over large areas of the body.
- Swelling: In some cases, swelling may occur not only on the skin but also on the lips, tongue, or throat, signalling a more severe reaction.
- Burning or tingling sensation: Some people experience burning or tingling sensations on the affected skin.
- Redness and warmth: The skin around the hives may appear red and warm to the touch.
Severe Reactions (Anaphylaxis)
In rare circumstances, a strawberry allergy can lead to a serious allergic reaction called anaphylaxis, which requires immediate medical attention. Symptoms of anaphylaxis may include:
- Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath.
- Swelling of the face, lips, or throat (angioedema).
- Dizziness or fainting.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Increased heart rate.
If anaphylaxis is suspected, it is crucial to seek emergency medical attention immediately.
Strawberry Hives Treatment
Treatment for strawberry-induced hives depends on the severity of the symptoms. In mild cases, home remedies may be sufficient, while more severe reactions require medical intervention.
1. Antihistamines
Antihistamines are the most commonly used medications to treat hives. These drugs block the action of histamine, reducing itching and inflammation.
- Over-the-counter antihistamines: Medications such as cetirizine, loratadine, or diphenhydramine can help reduce symptoms.
- Prescription antihistamines: If symptoms are persistent or severe, your doctor may prescribe stronger or longer-acting antihistamines.
Tip: Antihistamines can cause drowsiness, so it is important to read labels carefully and consult a doctor before use.
2. Corticosteroids
If hives are severe or don’t respond to antihistamines, your doctor may prescribe oral or topical corticosteroids to reduce inflammation. Corticosteroids are usually used for short periods of time due to their side effects.
3. Natural remedies
Some natural remedies can help reduce the itching and swelling associated with hives.
Cold compresses
Cold compresses can reduce swelling and itching, providing temporary relief.
How to use them:
- Wrap ice in a cloth and apply it to the affected areas for 10-15 minutes.
- Repeat the operation several times a day.
Colloidal oatmeal
- Colloidal oatmeal baths are known for their soothing properties and can relieve itching.
How to use it:
- Add a cup of colloidal oatmeal to your bath water and soak for 15-20 minutes.
- Be sure to use lukewarm, not hot, water to avoid further irritating your skin.
Aloe Vera
- Aloe vera has anti-inflammatory properties and can be applied topically to reduce itching and inflammation.
How to use it:
- Apply Aloe Vera gel directly to the affected skin and leave it on until completely absorbed.
4. Epinephrine (adrenaline)
For severe allergic reactions such as anaphylaxis, epinephrine is the emergency treatment of choice. Epinephrine helps quickly reverse severe symptoms, such as throat swelling and difficulty breathing.
- If you have a history of severe food allergies, your doctor may recommend that you always carry an epinephrine auto-injector (such as an EpiPen) with you in case of an emergency.
Strawberry Hives Prevention
Prevention of strawberry hives is mainly based on avoiding the consumption of strawberries and strawberry products if you are sensitive to this fruit.
1. Avoid strawberries and strawberry products
If you’ve ever experienced hives or other allergic symptoms after eating strawberries, you should completely avoid the fruit, including juices, jams, or desserts containing strawberries
2. Read food labels carefully
Many food products may contain strawberry extracts or natural flavours. Carefully reading the labels on packaged foods is essential to avoid accidentally consuming strawberries.
3. Be careful with cross-contamination
Strawberries can be cross-contaminated with allergens, such as when preparing dishes containing other fruits. Make sure the utensils and dishes you use to prepare your meals have not been in contact with strawberries.
Summary Table
Characteristic | Description |
Main causes | Strawberry protein allergy, natural histamine, chemical additives |
Common symptoms | Red bumps, itching, swelling, redness, tingling |
Main treatments | Antihistamines, corticosteroids, epinephrine (for severe reactions) |
Natural Remedies | Cold compresses, baths with colloidal oatmeal, Aloe Vera |
Prevention | Avoid consuming strawberries, read labels, and avoid cross-contamination. |