Tonsillitis: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, and Home Remedies for Quick Relief
Introduction
Tonsillitis is a common infection, especially among children, though adults can also be affected. While it’s often self-limiting, in some cases, it can lead to severe complications if left untreated. This article provides a detailed overview of tonsillitis, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, home remedies, and treatment options.
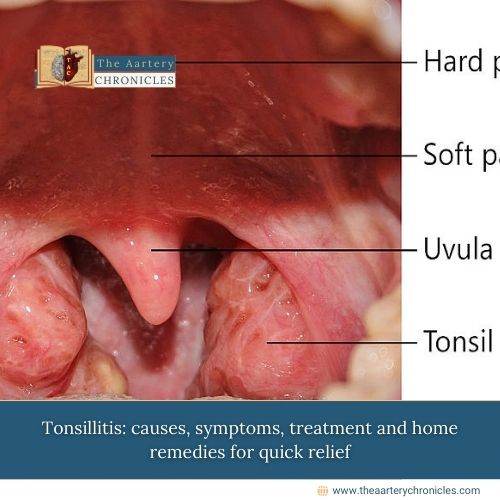
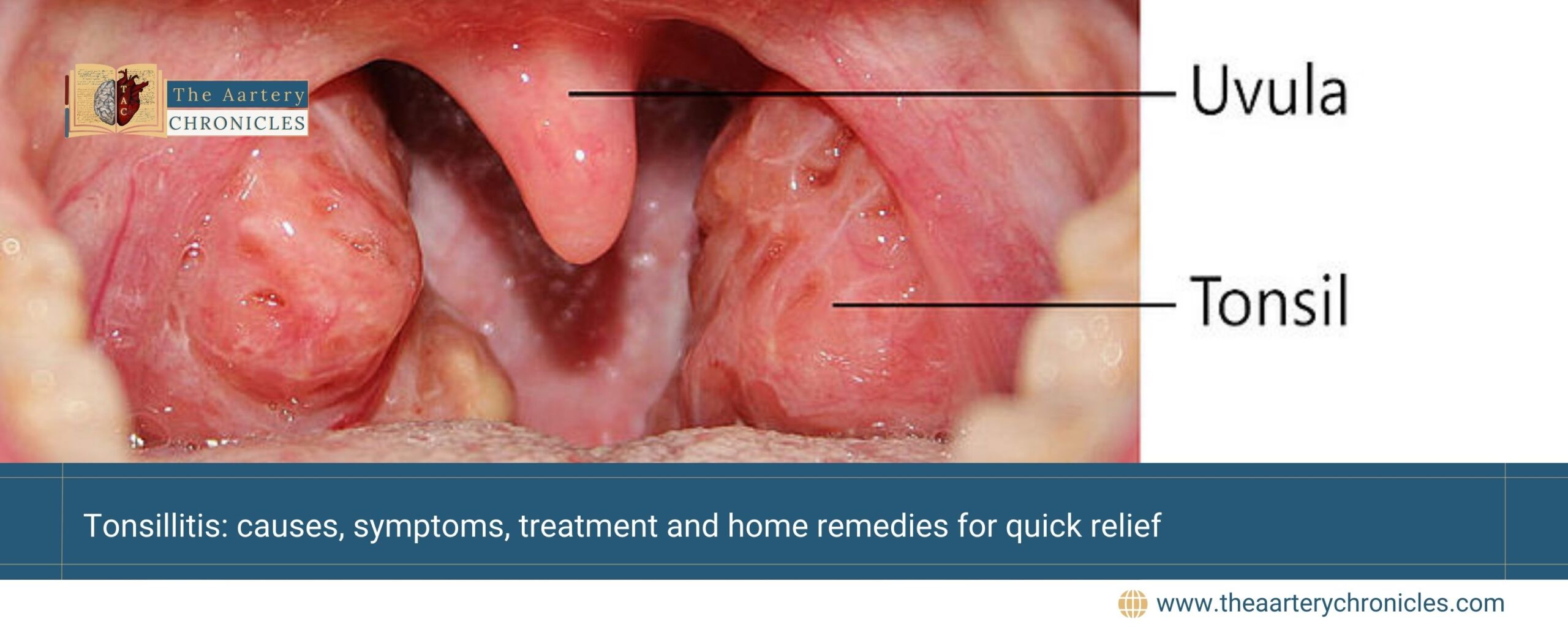
What are Tonsils?
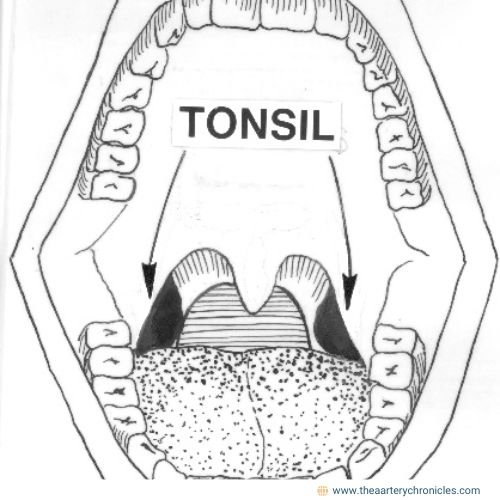
Tonsils are two small, oval-shaped masses of lymphoid tissue located at the back of the throat (oropharynx), one on either side of the throat.
- They are part of the immune system, acting as a defense system to filter and trap bacteria, viruses, and harmful substances entering through the mouth or nose.
- Tonsils help produce white blood cells and antibodies to fight infections.
- They are most active between the ages of 4 and 10 when children are more susceptible to infections.
- After puberty, tonsils begin to shrink (involution) as the body’s immune system matures and becomes more efficient.
- Tonsils, along with the adenoids and lingual tonsils, form Waldeyer’s Ring, a group of lymphoid tissues that provide a protective barrier.
- While they play a critical role in early immune function, tonsils can become infected, leading to tonsillitis.
What is Tonsillitis?
Tonsillitis is the inflammation and infection of the tonsils, characterized by swelling, pain, and redness in the throat.
- It is most commonly seen in children aged 5 to 15 but can also affect adults.
- While tonsillitis often begins as a viral infection, such as from rhinovirus or adenovirus, it can also be caused by bacterial infections.
Causes of Tonsillitis
Tonsillitis can arise from viral and bacterial infections, leading to inflammation of tonsils and discomfort in the throat.
Viral Infections:
- Common viral agents include:
- Rhinovirus
- Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)
- Adenovirus
- Epstein-Barr virus
- Common viral agents include:
Bacterial Infections:
- Most frequently implicated bacteria:
- Group A beta-hemolytic Streptococcus (causes strep throat)
- Other bacterial causes:
- Staphylococcus
- Pneumococcus
- Haemophilus influenzae
- Most frequently implicated bacteria:
Modes of Transmission
- Infections spread through tiny droplets released into the air by:
- Sneezing
- Coughing
- Healthy individuals can become infected when these droplets come into contact with their mucous membranes.
Symptoms of Tonsillitis
Tonsillitis presents with a range of symptoms, which may vary in severity depending on the cause and individual response. Common symptoms include:
- Sore throat
- Red, swollen tonsils
- Fever
- Headache
- Scratchy or muffled voice
- Halitosis (bad breath)
- Odynophagia (painful swallowing due to local throat pain)
- Earache (caused by referred pain through the glossopharyngeal nerve)
- Enlarged lymph nodes in the neck
- Abdominal pain (due to mesenteric lymphadenitis)
- In severe cases, episodes of obstructive sleep apnea may occur, affecting breathing during sleep.
Diagnosis of Tonsillitis
Tonsillitis is primarily diagnosed through a clinical examination by a healthcare provider. The healthcare provider will ask about the patient’s symptoms, such as sore throat, fever, and difficulty swallowing.
Local Examination:
- The doctor will check for redness, swelling, yellowish/white spots, or membranes over the tonsils.
- The neck will be examined for enlarged lymph nodes, which can indicate infection.
Differentiating Viral vs. Bacterial Infection:
It is essential to distinguish between viral and bacterial tonsillitis to avoid unnecessary use of antibiotics.
To do this, the following tests may be recommended:
Throat Swab Tests:
- Rapid Strep Test: Provides results in a few minutes. A negative result does not completely rule out strep throat.
- Throat Culture: More reliable but takes a few days for results. It confirms the presence of bacterial infections, particularly Group A Streptococcus.
Home remedies for Tonsillitis
Tonsillitis can be uncomfortable, but certain home remedies can provide relief, especially for viral infections that resolve on their own:
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of fluids (cold or warm) to soothe the throat.
- Eat Soft Foods: A soft, bland diet reduces throat discomfort during meals.
- Gargle with Salt Water: Warm salt water can reduce pain and inflammation.
- Throat Lozenges: Help soothe a sore throat (not recommended for children under 4 to avoid choking).
- Honey and Tea: Honey has antimicrobial properties, and warm tea can provide relief.
- Ginger Tea: Known for its anti-inflammatory effects, ginger tea may help reduce swelling.
- Popsicles: Frozen treats can be a great way to relieve throat pain in children.
- Use a Humidifier: Moist air can reduce throat irritation caused by dry environments.
Risks of Leaving Tonsillitis Untreated
Leaving tonsillitis untreated can emerge as a serious health hazard for you as well as your dear ones. Untreated tonsillitis can result in the following potentially dangerous conditions:
- Peritonsillar Abscess: A painful pus-filled swelling near the tonsils, which may require drainage and can obstruct breathing.
- Exanthematous Reactions: Skin rashes that can occur as a reaction to the underlying infection.
- Septicemia: A severe bloodstream infection that can spread throughout the body, leading to organ failure and potentially death.
- Glomerulonephritis: Inflammation of the kidney’s filtering units, which can follow a streptococcal infection and may lead to chronic kidney disease.
- Rheumatic Fever: A serious complication of untreated strep throat that can cause inflammation in the heart, joints, skin, and brain. Long-term consequences may include valvular heart disease.
- Lemierre’s Syndrome: A rare but life-threatening condition involving infectious thrombophlebitis (blood clot and infection) of the internal jugular vein, which can result in severe systemic infection.
It is crucial to seek timely medical treatment for tonsillitis to prevent these life-threatening complications.
Medical Treatment for Tonsillitis
The treatment approach for tonsillitis varies based on whether the infection is viral or bacterial:
Pain Relief:
- Over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen are recommended to alleviate fever and throat pain.
Antibiotics (for bacterial tonsillitis):
- A full course of antibiotics is crucial to prevent recurrence and complications.
- Oral penicillin for 10 days is the most common treatment.
- For patients who struggle with adherence to the oral regimen, a single shot of intramuscular benzathine penicillin G may be administered.
- For individuals allergic to penicillin, azithromycin is the recommended alternative.
Corticosteroids:
- In severe cases, corticosteroids may be prescribed to reduce throat swelling and inflammation, helping to ease discomfort and speed up recovery.
Treatment aims to relieve symptoms, prevent complications, and reduce the spread of the infection.
When Is Tonsillectomy Necessary?
Tonsillectomy, or surgical removal of the tonsils, is recommended in cases of recurrent or severe tonsillitis. The criteria for surgery include:
- Recurrent Tonsillitis:
- 3 or more episodes per year over the last 3 years
- 5 or more episodes per year over the last 2 years
- 7 or more episodes in the last year
Other factors considered include the
- Severity of the illness
- Missed school or work due to frequent infections
- Recurrent sleep apnea episodes that impact quality of life.
Recovery from tonsillectomy typically takes around two weeks, with full healing and symptom relief expected after that period.
Conclusion
Tonsillitis presents a range of symptoms that can affect daily activities and well being of an individual. With prompt diagnosis and treatment, this condition can be managed effectively along with reducing the risk of complications, leading to better overall health and quality of life. If you’re experiencing frequent bouts of tonsillitis, consult your healthcare provider for the best course of action.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Can adults get tonsillitis?
Yes, though it is more common in children, adults can also get tonsillitis. - How can I prevent tonsillitis?
Good hygiene practices, such as washing hands regularly and avoiding close contact with sick individuals, can reduce the risk of tonsillitis. - What foods should be avoided during tonsillitis?
Spicy, hard, or crunchy foods that can irritate the throat should be avoided. Stick to soft and soothing foods like soup or yogurt.

Dr Varsha Attri
MBBS
I’m a dedicated MBBS doctor with a strong passion for medical research. After graduating from SGRD University Of Health Sciences and working as a medical officer, I realized my passion for medical writing. I thrive on continuous learning and seek to expand my knowledge and skills in the field of Medical Journalism. Outside of medicine, I enjoy reading books and connecting with nature which fuel my creativity and inspire my writing. I’m eager to contribute meaningful content that informs and educates others in healthcare.








